- Authors
- Written by :
- Name
- Varun Kumar
The Ultimate Checklist: On-Page SEO essentials for Web Applications
- Published on
- Published On:
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is a digital marketing strategy aimed at increasing the quantity and quality of website traffic by ranking higher in search engine results pages (SERPs) for specific keywords or phrases. It involves understanding how search engines work, what people search for, and the keywords and phrases they use.
This blog serves as a checklist of all the essential On-Page SEO techniques any web application should have to gain the following benefits:
- Increased organic traffic and increased visibility: ranking higher in search result leads to greater visibility, and you attract more visitors who are genuinely interested in your content or offerings.
- Improved brand awareness: Higher visibility in search results can lead to greater brand recognition.
- Cost-effective marketing: SEO is an ongoing process, but it's a cost-effective way to attract qualified leads compared to paid advertising.
- Credibility and Trust: Websites that rank higher are often perceived as more credible and trustworthy by users.
- Competitive Advantage: Effective SEO can help you stay ahead of competitors by attracting more traffic and potential customers.
- Improved User Experience: Many SEO practices, such as faster page load times and mobile optimization, enhance the overall user experience.
SEO encompasses a variety of techniques and best practices that can be categorized into three main areas: On-Page SEO, Off-Page SEO, and Technical SEO. In this blog we will mostly discuss about On-Page SEO techniques your application should have.
What is On-Page SEO?
On-Page SEO refers to the practice of optimizing web pages to improve a website's search engine rankings and earn organic traffic. Unlike Off-Page SEO, which involves external factors like backlinks and social signals, On-Page SEO focuses on optimizing elements within the website itself. These elements include content quality, HTML source code, and overall website structure.
Mentioned below is a checklist of the most important points to have in your web application to make On-Page SEO work for your business.
On-Page SEO essentials checklist
A) High-Quality Content: Creating Compelling, Informative, and Engaging Content
High-quality content is the bedrock of successful On-Page SEO. It encompasses creating content that not only ranks well in search engine results but also genuinely engages and informs your audience.
High-quality content delivers value to the reader. Here's how you can ensure your content is valuable:
- Informative: Your content should be well-researched, accurate, and comprehensive. It should provide all necessary information to answer the reader's query fully.
- Actionable: Offer practical advice or steps that readers can follow. For example, in a "how-to" guide, break down the process into easy-to-follow steps with clear instructions.
- Engaging: Make your content interesting to read. Use storytelling techniques, incorporate real-life examples, and add a personal touch. Engaging content keeps readers on your page longer and reduces bounce rates.
- Comprehensive: Cover the topic thoroughly, addressing various aspects and potential questions the reader might have. Long-form content often performs better because it's seen as more authoritative and informative.
- Unique: Provide unique insights or perspectives that aren't readily available elsewhere. Original research, personal experiences, and unique takes on a subject can set your content apart from competitors.
B) Avoid Plagiarism
Plagiarism refers to the practice of copying content from other sources without proper attribution. This can include direct copying, paraphrasing without credit, or even republishing the same content on multiple sites (also known as duplicate content).
Search engines strive to provide users with original, high-quality content, and they have developed sophisticated mechanisms to detect and penalize plagiarism. They aim to provide users with original and valuable content, so they actively penalize websites that engage in plagiarism.
Engaging in plagiarism can have severe consequences for your website's SEO, including:
- Lower Rankings: Search engines prioritize original content. If your content is found to be plagiarized, your site can be pushed down in the search rankings.
- De-indexing: In severe cases, search engines may completely remove a website from their index, meaning it won't appear in search results at all.
- Penalties: Websites caught plagiarizing content may receive manual penalties from search engines, which can be difficult to recover from.
- Loss of Trust: Both users and search engines value originality. Plagiarized content can damage your site's reputation and erode user trust.
C) All pages must have a page title <title>
A page title, defined by the <title> HTML tag, is a critical component of on-page SEO. It serves multiple purposes, from influencing search engine rankings to enhancing user experience. Here's an in-depth look at why all pages must have a page title and best practices for crafting effective titles.
Best Practices for Crafting Effective Page Titles
- Include Primary Keywords: Use relevant keywords that accurately describe the content of the page. Place the primary keyword near the beginning of the title for better SEO impact.
- Keep it Concise: Search engines typically display the first 50-60 characters of a title tag.
- Make it Descriptive: The title should accurately describe the page's content so users know what to expect when they click.
- Add Branding: If appropriate, include your brand name at the end of the title tag. This can help build brand recognition and trust (example “ | Crownstack”).
- Avoid Keyword Stuffing: While it's important to include keywords, avoid overloading the title with them. This can lead to a negative user experience and potential penalties from search engines.
- Use Unique Titles: Ensure each page on your website has a unique title to avoid confusion for both users and search engines. Duplicate titles can dilute the effectiveness of your SEO efforts.
D) Include heading tags
Heading tags, ranging from <h1> to <h6>, play a crucial role in structuring web content and enhancing both SEO and user experience. These tags help search engines understand the hierarchy and relevance of content on a webpage, while also making the content more readable and navigable for users.
Heading tags are HTML elements used to define headings and subheadings within your content. There are six levels of heading tags, from <h1> to <h6>, with <h1> being the most important and <h6> the least important. Each tag serves a different purpose in organizing and presenting content:
<h1>: The main heading of the page, typically used once per page.<h2>to<h6>: Subheadings that help organize content into sections and subsections, with decreasing importance.
E) Make your URLs SEO-friendly
An SEO-friendly URL is a web address that is optimized to be easily read by both humans and search engines. These URLs are important for improving search engine rankings, enhancing user experience, and increasing the likelihood of click-throughs from search engine results pages (SERPs). This article explores the characteristics of SEO-friendly URLs, why they are important, and best practices for creating them.
An SEO-friendly URL is structured in a way that clearly conveys the content of the page. It is simple, descriptive, and includes relevant keywords without being overly complex. Here's an example to illustrate:
- SEO-Friendly URL:
https://www.yourwebsite.com/categories/smart-watches - Non-SEO-Friendly URL:
https://www.yourwebsite.com/categories/37
The SEO-friendly URL is short, descriptive, and easy to understand, while the non-SEO-friendly URL is complicated and provides no information about the page content.
F) Inter-linking pages within the website
Inter-linking, also known as internal linking, refers to the practice of linking one page of a website to another page within the same website. This technique is a crucial aspect of on-page SEO and plays a significant role in improving a website's search engine optimization, enhancing user experience, and facilitating site navigation.
Inter-linking involves creating hyperlinks that connect different pages of the same website. These links are typically embedded within the content using anchor text, which is the clickable text in a hyperlink. For example, a blog post on "Crownstack's Git Workflow" might include a link to another post on "The art of managing github repositories"
G) Make mobile responsive designs
Mobile responsive design refers to a web design approach that ensures a website's layout, content, and performance adapt seamlessly to various screen sizes and devices. A mobile responsive website is crucial for enhancing user experience and optimizing search engine performance.
Mobile responsive design involves using flexible grids, layouts, images, and CSS media queries to create a website that provides an optimal viewing experience across a wide range of devices. Whether accessed on a desktop, tablet, or smartphone, a mobile-responsive website adjusts its elements to fit the screen size and resolution, ensuring usability and readability.
H) Best Practices for Implementing Mobile Responsive Design
- Flexible Layouts:
- Fluid Grids: Use fluid grid layouts that resize elements proportionally based on the screen size. This ensures that the design remains consistent across different devices.
- Flexible Images: Ensure images resize within their containing elements. Use CSS techniques like
max-width: 100%to make images responsive.
- Media Queries:
- CSS Media Queries: Implement CSS media queries to apply different styles based on the device's screen size and orientation. This allows for tailored designs for various devices.
- Breakpoints: Define breakpoints at which the design changes to accommodate different screen sizes. Common breakpoints include those for smartphones, tablets, and desktops.
- Responsive Typography:
- Scalable Fonts: Use scalable units like
emorremfor font sizes, ensuring text remains readable on all devices. - Line Height and Spacing: Adjust line height and spacing to improve readability on smaller screens.
- Scalable Fonts: Use scalable units like
- Touch-Friendly Design:
- Clickable Elements: Make buttons and links large enough for touch interactions. Ensure there is enough space between interactive elements to prevent accidental clicks.
- Gestures: Consider incorporating touch gestures like swiping for better mobile navigation.
- Performance Optimization:
- Fast Loading Times: Optimize images, minify CSS and JavaScript, and leverage browser caching to improve loading times on mobile devices.
- AMP: Consider implementing Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) for faster loading and better mobile performance.
- Viewport Meta Tag:
- Viewport Configuration: Include the viewport meta tag in your HTML to control the layout on mobile browsers. This ensures the page scales correctly on different devices.
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
- Viewport Configuration: Include the viewport meta tag in your HTML to control the layout on mobile browsers. This ensures the page scales correctly on different devices.
I) Ensure Faster loading times
Page load speed affects how quickly users can access and interact with your website, and it is a significant factor in search engine rankings. Slow-loading pages frustrate users, leading them to abandon the site.
Best Practices for Optimizing Page Speed
- Optimize Images and other multimedia:
- Compression: Compress images without losing quality using tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim.
- Responsive Images: Use responsive images that adjust based on the user's device and screen size.
- Proper Formats: Use modern image formats like WebP, which offer better compression and quality compared to traditional formats like JPEG and PNG.
- Leverage Browser Caching:
- Cache Static Resources: Set long expiration times for static resources like images, CSS, and JavaScript files. This allows returning visitors to load your site faster by fetching files from their local cache.
- Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML:
- Remove Unnecessary Code: Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML files to remove unnecessary characters like spaces and comments, reducing file sizes.
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN):
- Distributed Servers: CDNs store copies of your site on servers around the world, reducing latency and improving load times for users regardless of their geographical location.
- Reduced Server Load: CDNs distribute traffic across multiple servers, reducing the load on your origin server and improving site performance.
- Optimize Server Response Time:
- Efficient Hosting: Choose a reliable and fast hosting provider. Consider using dedicated or virtual private servers (VPS) instead of shared hosting.
- Database Optimization: Optimize your database by regularly cleaning up unnecessary data and using efficient queries.
- Implement Lazy Loading:
- Defer Offscreen Content: Use lazy loading to defer the loading of images and other non-critical resources until they are needed. This reduces initial load times and improves perceived performance.
- Enable Compression:
- Gzip/Brotli Compression: Enable Gzip or Brotli compression on your server to reduce the size of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files, speeding up load times.
- Reduce Redirects:
- Minimize Redirect Chains: Avoid unnecessary redirects and minimize redirect chains, as each redirect adds latency and slows down page loading.
J) Having Alt text for all the images
Alt text (alternative text) is a crucial element of on-page SEO that serves both accessibility and search engine optimization purposes. It provides a textual description of images on a webpage, which helps search engines understand the content and context of images.
Alt text is an HTML attribute added to image tags (<img>) that provides a textual description of the image. The primary purposes of alt text are:
- Accessibility: Alt text helps visually impaired users understand the content of images through screen readers.
- SEO: Alt text allows search engines to index and understand the images, contributing to better search rankings and image search visibility.
K) Meta tags
Meta tags are HTML elements that provide metadata about a webpage. They do not appear on the webpage itself but rather in the page's source code. Meta tags serve various purposes, including helping search engines understand the content of a page, improving SEO, and influencing how content is displayed in search engine results pages (SERPs).
Meta description tag
- Purpose: The meta description tag (
<meta name="description" content="...">) provides a brief summary of the webpage's content. - Importance: It influences click-through rates (CTR) from search engine results by giving users a preview of what to expect on the page.
- Best Practices: Keep it concise (typically 150-160 characters), include relevant keywords, and make it compelling to encourage clicks.
Open Graph (OG) tags
Open Graph (OG) tags are meta tags that enable control over how URLs are displayed when shared on social media platforms like Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter etc. They allow web developers to specify which images, titles, descriptions, and other elements should appear when a URL is shared, enhancing the visibility and engagement of shared content.
Some of the most important and effective Open Graph tags are:
og:title
og:titleis a meta tag attribute used to specify the title of a webpage or content piece when shared on social media platforms.- If not specified in page, social media websites use the content of
<title>tag. - Keep the
og:titleunder 60 characters to ensure it displays fully across different social media platforms without being truncated.
Example:
<meta
name="og:title"
content="”Automating"
Firebase
Cloud
Functions
deployment
using
CI
CD
pipeline”
/>
og:description
og:descriptionis a meta tag attribute used to provide a brief summary or description of a webpage or content piece when shared on social media platforms.
Example:
<meta
name="og:description"
content="”Automate"
the
code
deployments
for
multiple
environment
using
Github
Actions
with
Slack
Notifications.”
/>
og:image
og:imagestands as a crucial meta tag attribute designed specifically to define the image that represents a webpage or content piece when shared on social media platforms.- If not specified in the page, social media websites picks up the first image they found on the page.
- Also read our blog on "How to add dynamic Open Graph Images in Next.js"
Example:
<meta name="og:image" content=/static/images/blogs/web/the-ultimate-checklist-on-page-seo-optimization-for-web-applications/og-tags-link-preview.webp”>
og:url
og:urlis a meta tag attribute used to specify the canonical URL of a webpage or content piece when shared on social media platforms.- Canonical URLs refer to the preferred URL of a webpage among several URLs that might point to the same content. They are used primarily to address issues related to duplicate content and consolidate the ranking signals for search engines.
Example:
<meta name="og:url" content=”https://blog.crownstack.com/blog/web/automating_firebase_cloud_functions_deployment_using_ci_cd_pipeline”>
og:type
og:typeis a meta tag attribute used to specify the type of content being shared.og:typeallows you to categorize and define the type of content associated with a shared URL.
Example:
<meta name="og:type" content="”article”" />
Possible page types:
- music.song
- music.album
- music.playlist
- music.radio_station
- video.movie
- video.episode
- video.tv_show
- video.other
- article
- profile
- book
- profile
- website
Further reading: Link
An example preview how OG tags helps in rendering preview of links on Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter and others:
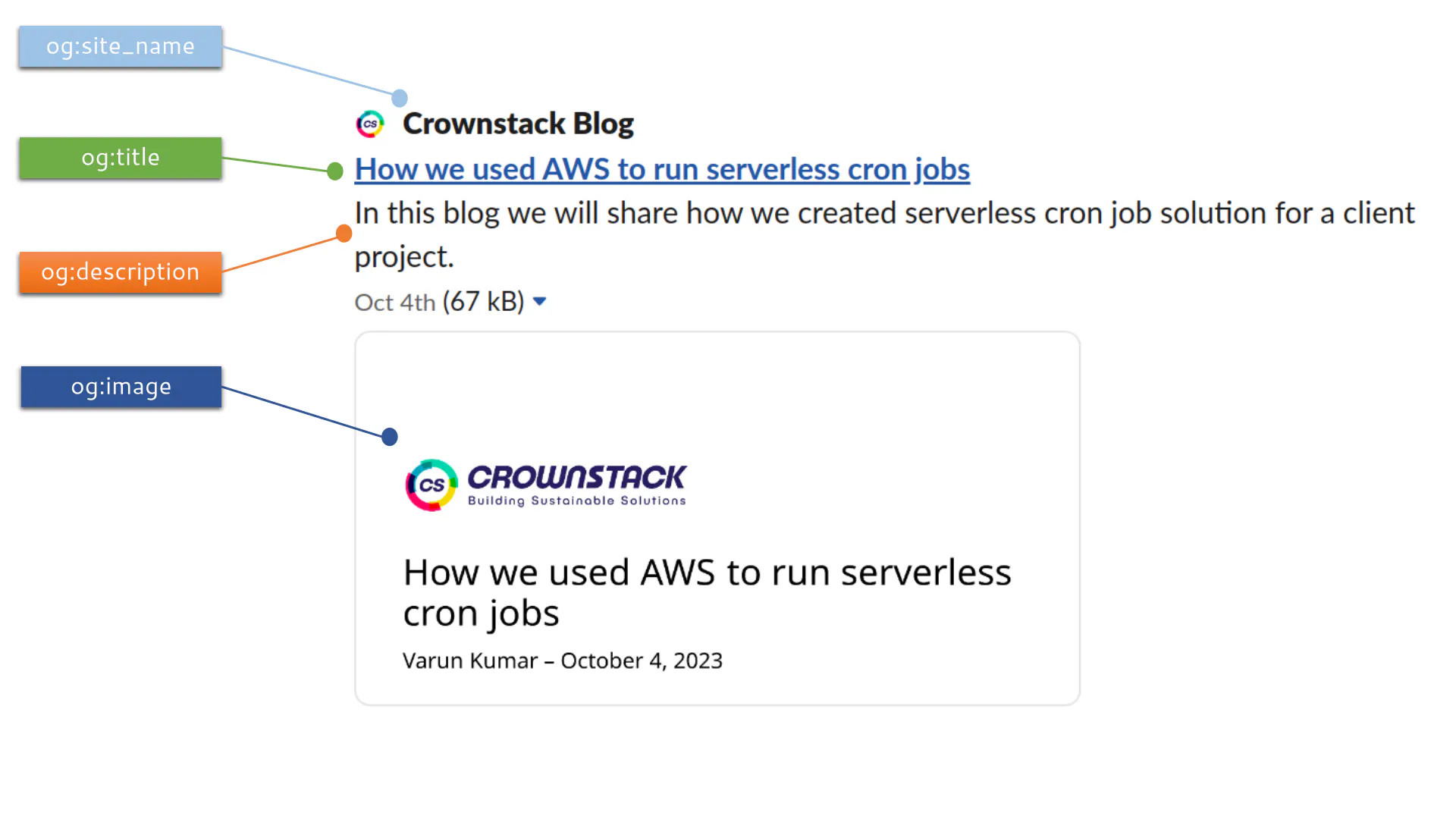
L) Twitter cards
Twitter Cards are a feature provided by Twitter that allow you to attach rich media, such as images, videos, and other content, to tweets. They enhance the appearance and functionality of tweets beyond the standard 280-character text limit, making it easier to engage and attract followers.
Types of Twitter Cards:
Summary Card:
- Description: Includes a title, description, thumbnail image, and Twitter account attribution.
- Best Use: Suitable for linking to blog posts, articles, or any content where a brief summary is sufficient.
Example:
<meta name="twitter:card" content="summary" />
Summary Card with Large Image:
- Description: Similar to the Summary Card but includes a larger image alongside the title and description.
- Best Use: Ideal for visually appealing content where the image plays a significant role in attracting attention.
Example:
<meta name="twitter:card" content="summary_large_image" />
App Card:
- Description: Highlights a mobile app with direct links to download from the App Store or Google Play.
- Best Use: Promoting mobile applications directly from Twitter with clear call-to-action buttons.
Example:
<meta name="twitter:card" content="app" />
Player Card:
- Description: Embeds audio or video media directly within the tweet, allowing users to play it without leaving Twitter.
- Best Use: Sharing multimedia content such as music, podcasts, or video clips directly on Twitter.
Example:
<meta name="twitter:card" content="player" />
Poll Card:
- Description: Enables creation of polls directly in tweets, allowing followers to vote and see real-time results.
- Best Use: Engaging followers with interactive polls on various topics or feedback gathering.
Example:
<meta name="twitter:card" content="poll" />
Once we decide which type of Twitter card we want to use, we insert appropriate <meta> tags in the <head> section of the webpage to specify the type of Twitter Card we want to display. Here's an example for a Summary Card with Large Image:
<meta name="twitter:card" content="summary_large_image" />
<meta name="twitter:site" content="https://twitter.com/crownstack" />
<meta
name="twitter:title"
content="Automating Firebase Cloud Functions deployment using CI/CD pipeline"
/>
<meta
name="twitter:description"
content="Automate the code deployments for multiple environment using Github Actions with Slack Notifications."
/>
<meta name="twitter:image" content="/static/images/Logo-light.png" />
Further reading: Link
M) Implementing Structured Data
Structured data refers to a standardized format for providing information about a webpage and classifying its content in a way that is easily understood by search engines and other web services. It uses a specific vocabulary (usually schema.org vocabulary) to mark up HTML elements on webpages, helping search engines interpret and display content more effectively in search results.
Structured data helps search engines better understand the relevance of a page to user queries, potentially leading to higher rankings and more relevant search results.
We can create structured data for:
- Article
- Book
- Breadcrumb
- Carousel
- Course
- Event
- Logo
- Product
- Reviews
- Video
If you want to learn more about how to implement structured data in your web application, read this documentation link from Google.
Final words
On-Page SEO is not just about appeasing search engine algorithms but also about creating a seamless and engaging experience for users. By implementing the techniques discussed in this blog, you can enhance your website's visibility, attract more targeted traffic, and ultimately achieve your business goals more effectively. Stay updated with the latest SEO trends and best practices to continually optimize your website and stay ahead of the competition in the digital landscape.
Mastering on-page SEO techniques is essential for enhancing your website's search engine performance, driving organic traffic, and ultimately achieving your digital marketing goals. By consistently implementing and refining these practices, businesses can improve their online presence, attract relevant audiences, and stay competitive in the dynamic digital landscape.
