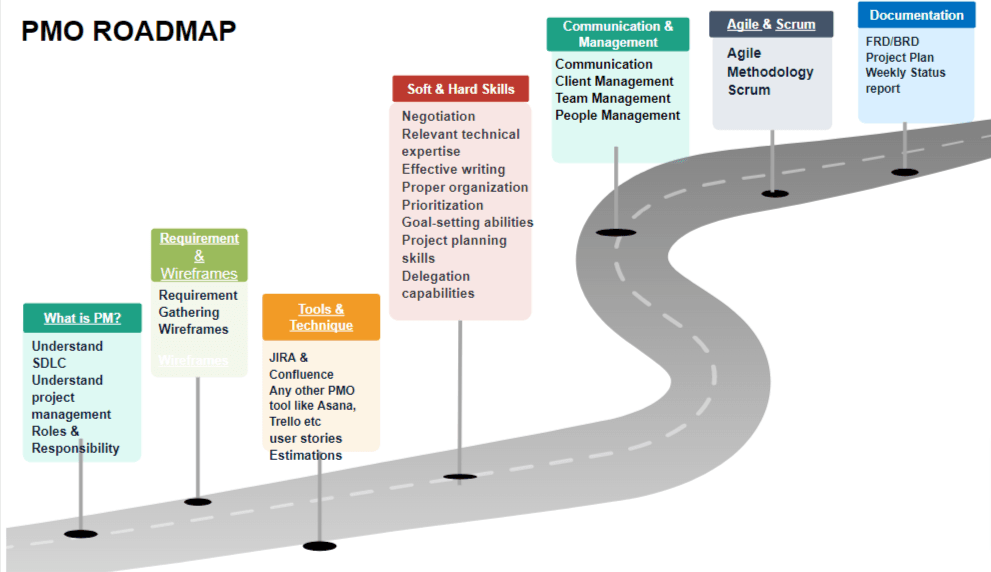
PM RoadMap
Project managers' diverse skill sets allow them to approach projects strategically and efficiently. After completing this learning path, you'll have the skills and knowledge to manage various projects from beginning to end using proven project management techniques.
The skill set and activities are very similar. You should gain experience in helping manage risks & issues, maintaining the project plan and writing project status reports. You also will gain experience dealing with the daily challenges a project faces.
Developing these skills will open up opportunities to take on other project roles, including business analyst, workstream lead and ultimately, project manager.
PROJECT MANAGEMENT
Project management is the discipline of planning, executing and completing projects. Project managers achieve this by using a set of methodologies, processes and tools to guide their teams and manage resources.
Today, most project management professionals use software to plan, execute, and control projects. Project Manager, for example, lets you manage plans, resources, costs and teams in one online tool.
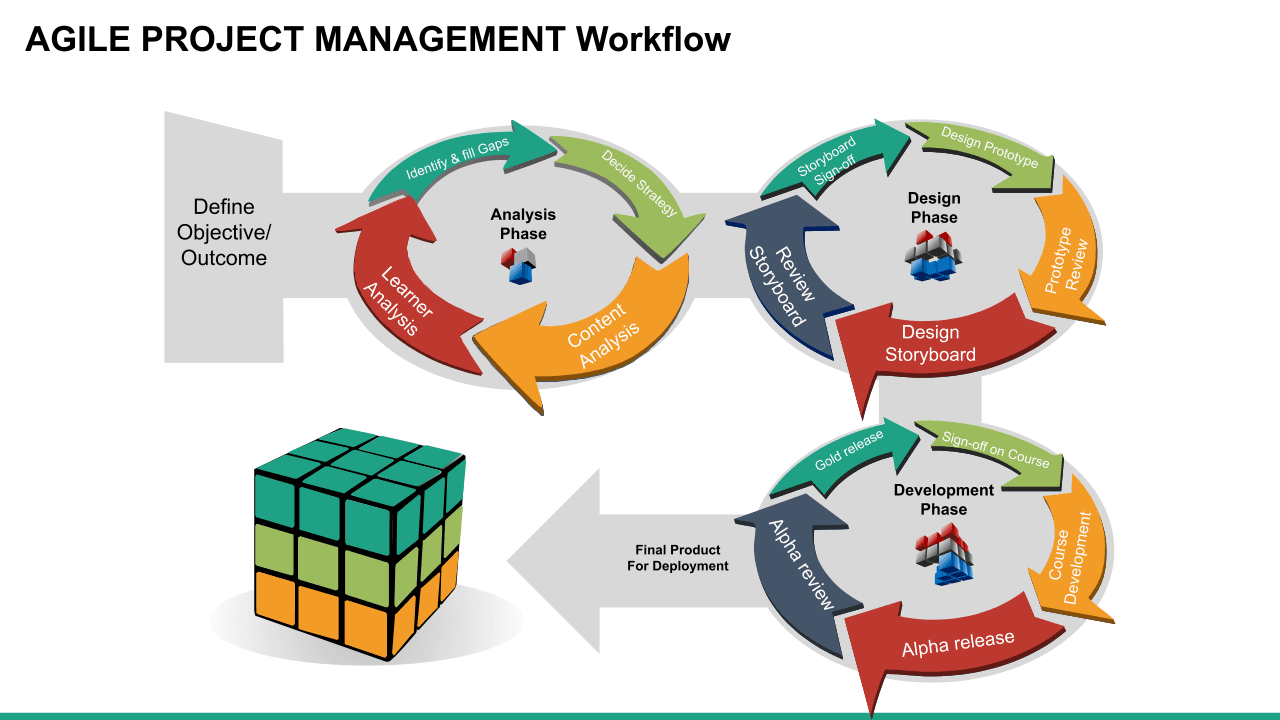
Understand SDLC:
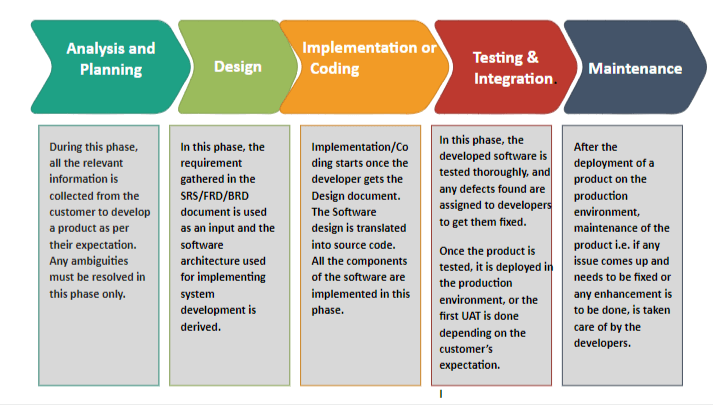
SDLC's 6 stages aim to deliver a high-quality product per the customer’s requirement. It’s a process of planning, writing, modifying, and maintaining software. Developers use the methodology as they design and write modern software for computers, cloud deployment, mobile phones, video games, and more. Adhering to the SDLC methodology helps to optimise the final outcome.
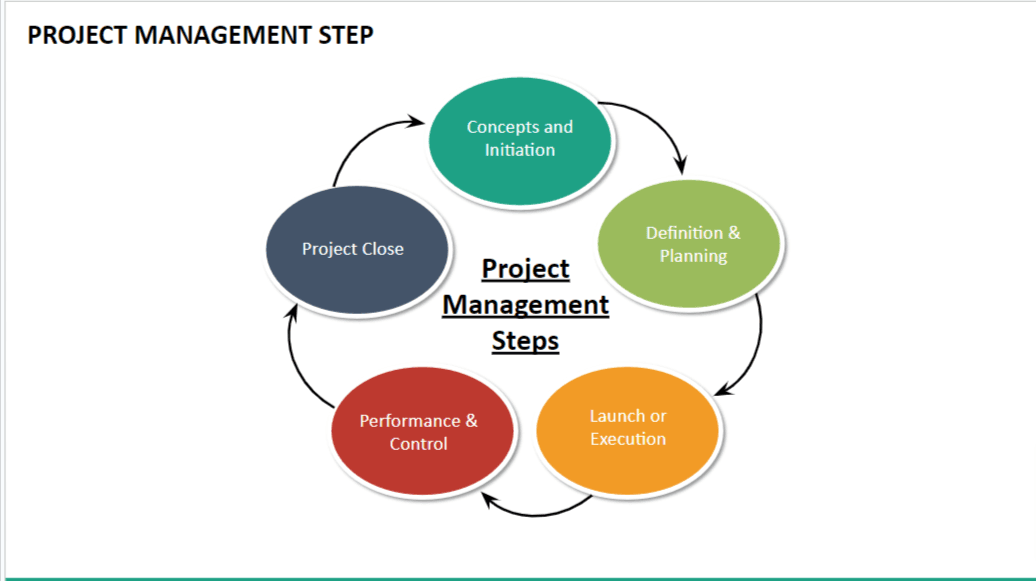
Project Management Steps:
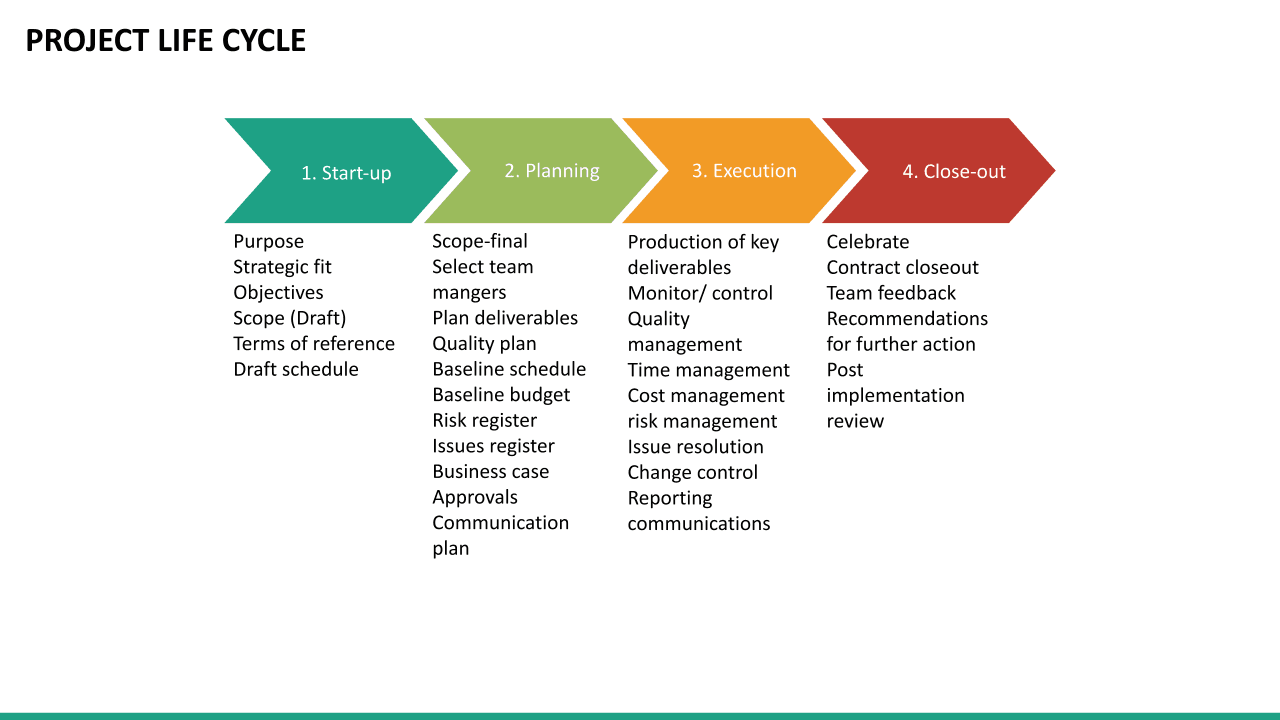
A project phase collects related project management activities. The relationship of the phases in the project life cycle is often sequential, and each phase culminates with completing one or more project deliverables.
The five phases of project management are
- Project Initiation
- Project Planning
- Project Execution
- Project Monitoring & Control
- Project Closure
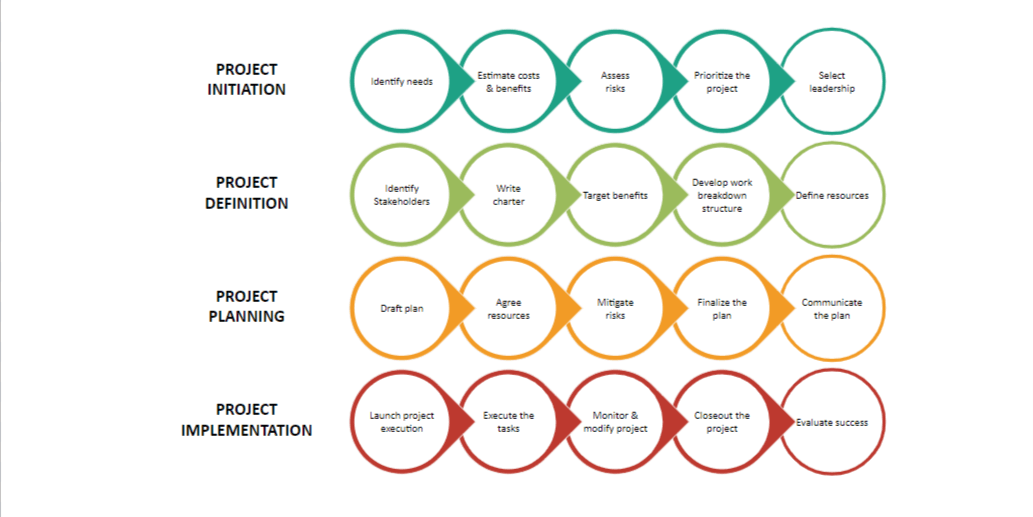
https://project-management.com/project-management-phases/
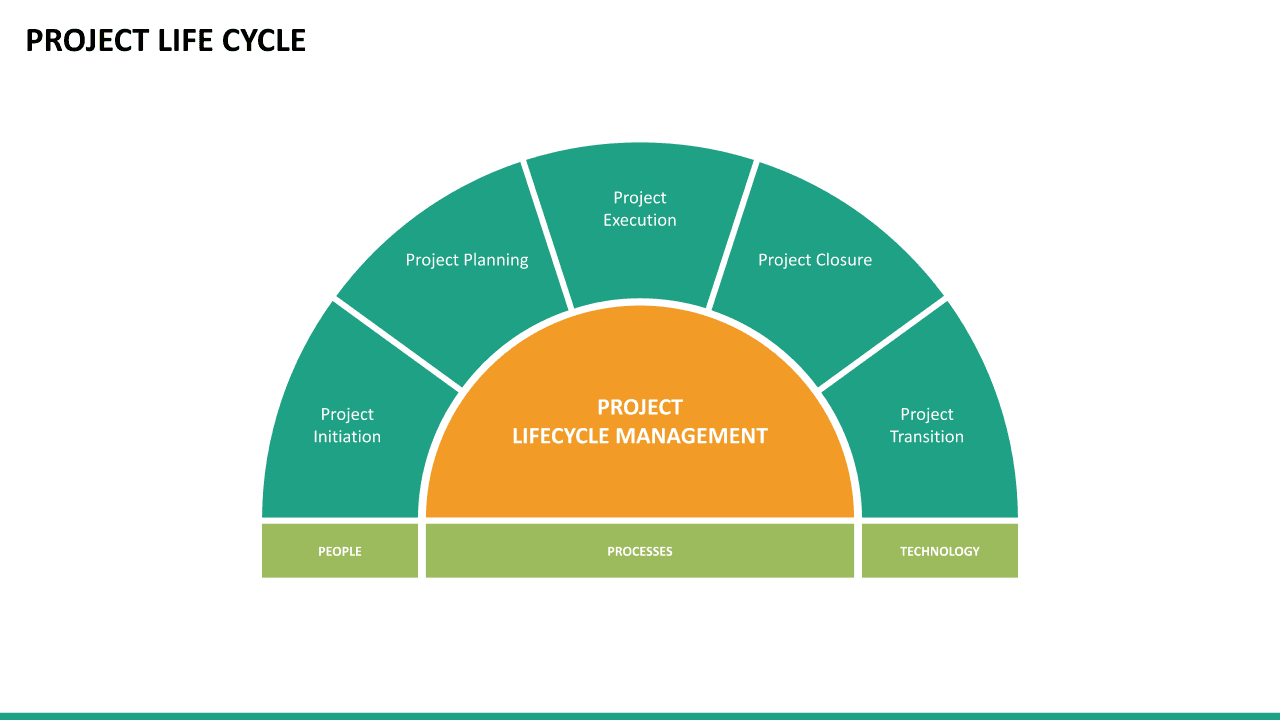
Project Lifecycle
The project life cycle comprises five project stages: project initiation, project planning, project execution, monitoring & control and project closing. Each of these phases is necessary for the effective delivery of the project.
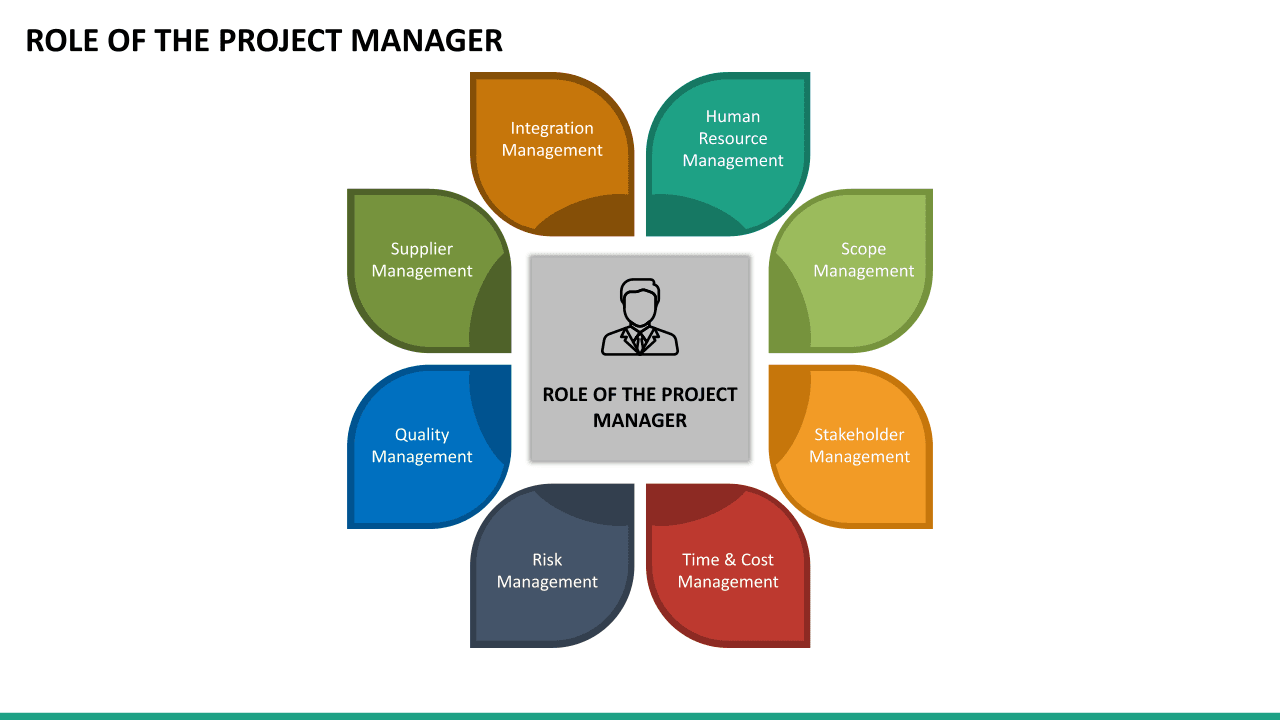
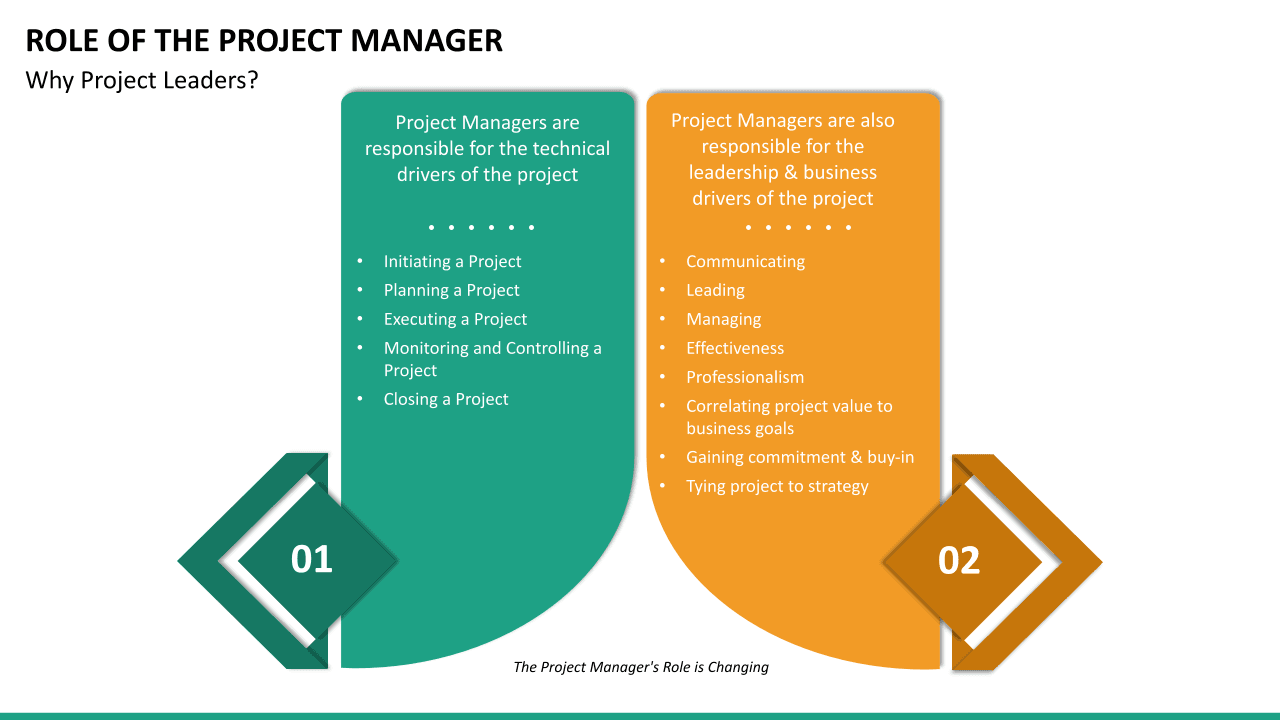
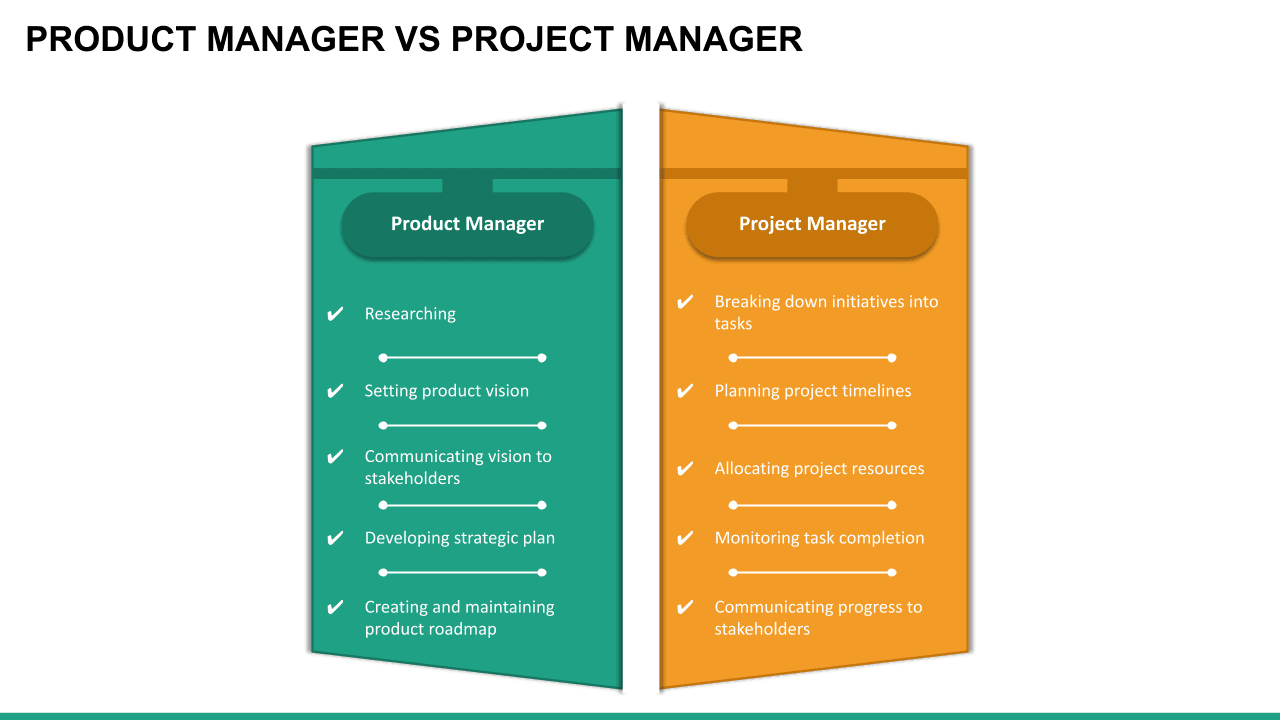
Project Manager Roles Responsibilities
A project manager is responsible for the direction, coordination, implementation, executive control and completion of the project while remaining aligned with the organisation's strategy, commitments and goals.’
Course Certifications in Project Management References
Tutorial: Project Management Study Material.
Requirement Gathering
A business requirement is a description of the features and functions of a product (something you will deliver) that satisfies a want or need…”
Why is it important?
Collecting requirements is the first step in creating a project scope management plan — which makes it one of the most critical steps toward a successful project.
However, eliciting stakeholder requirements is also one of the most challenging phases, as requirements often need to be more specific and easier to define.
Requirement gathering Techniques
Types of Documents & How to Create
Wireframes
Wireframing is a way to design a website service at the structural level. A wireframe is commonly used to lay out content and functionality on a page that considers user needs and journeys. Wireframes are used early in the development process to establish the basic structure of a page before visual design and content are added.
Wireframe Tools
- Sketch for detailed, vector-based design
- Adobe XD for beginners
- Figma for a free wireframe app
- UXPin for handing off design documentation to developers
- MockFlow for project organisation
- Justinmind for interactive wireframes
Reference links
Article 2
Agile & Scrum in Project Management
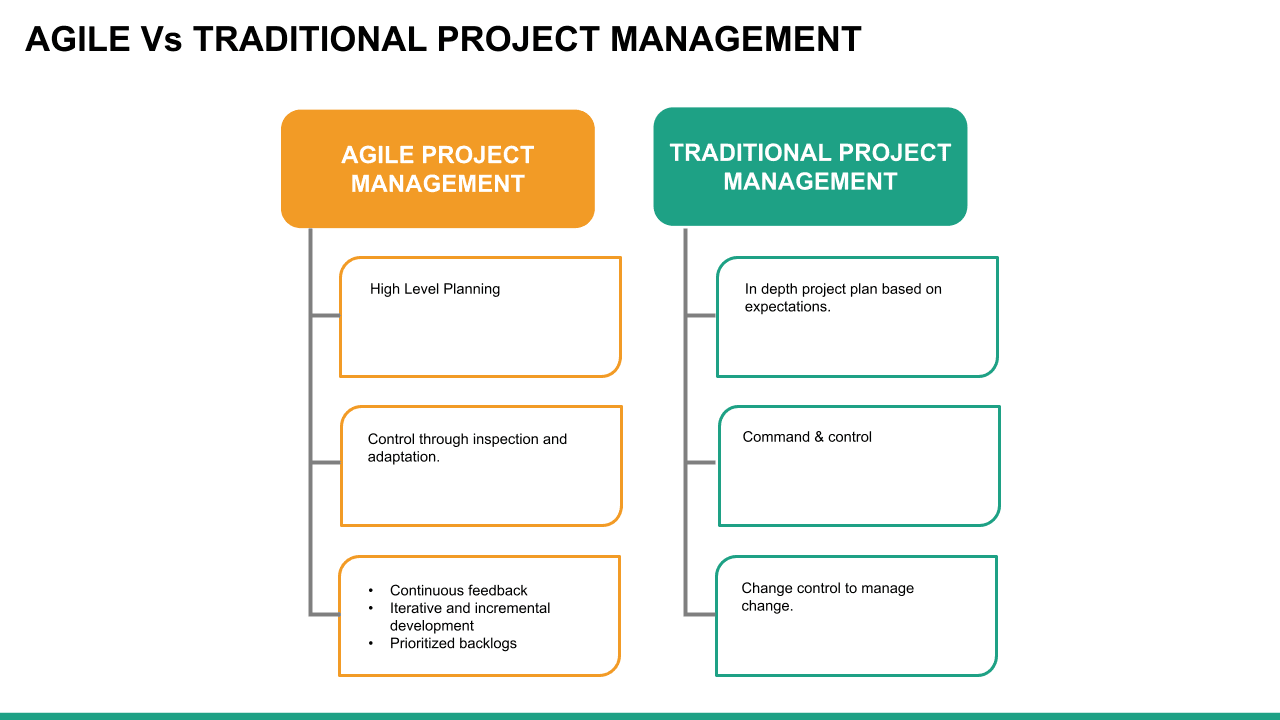
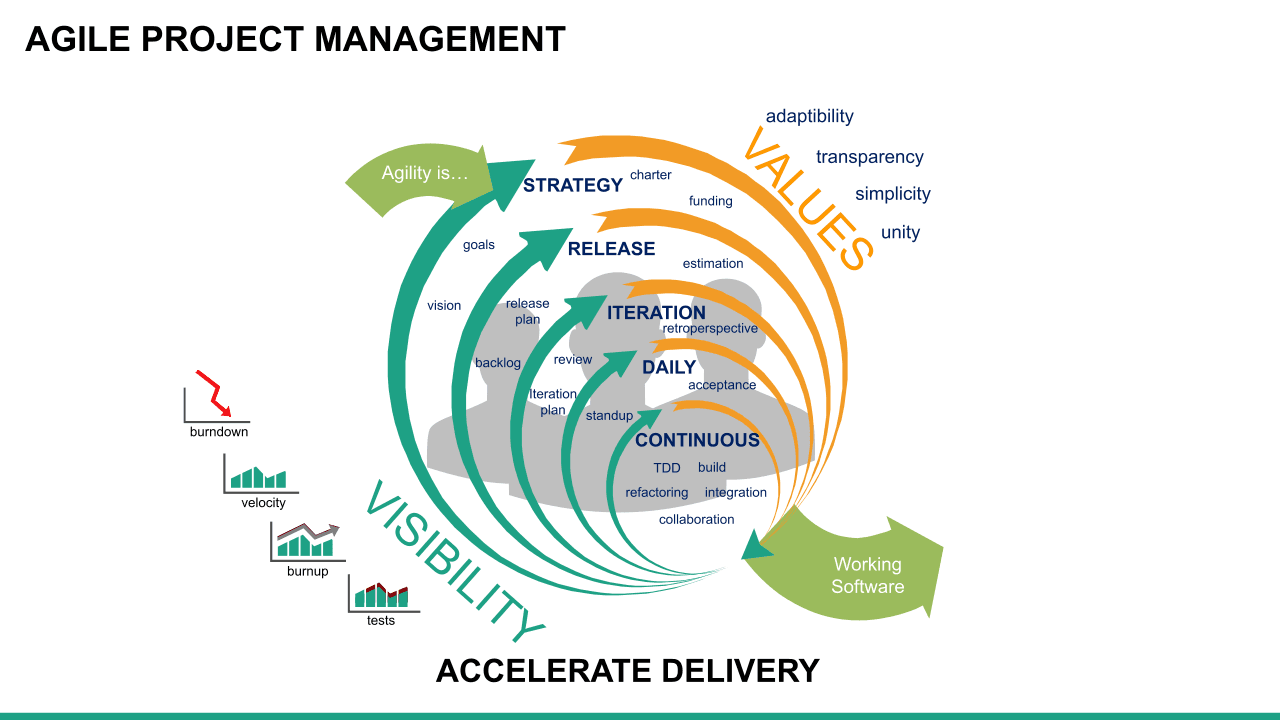
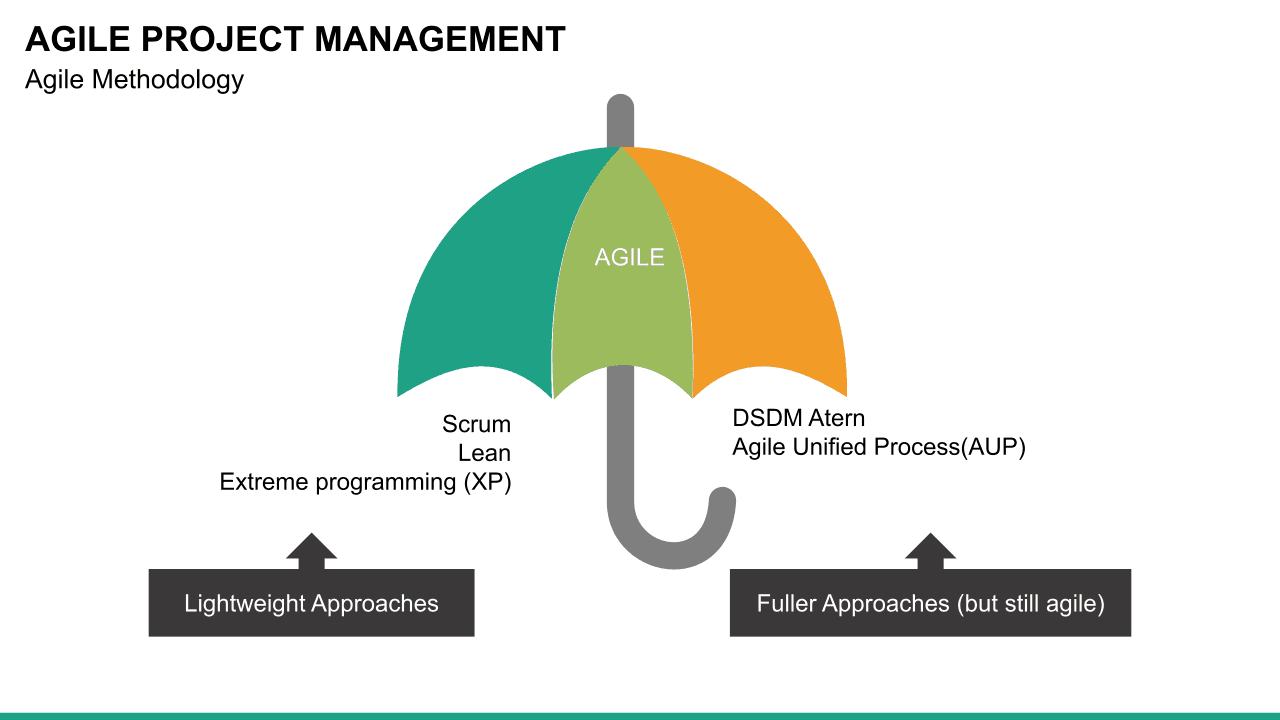
What is Agile?
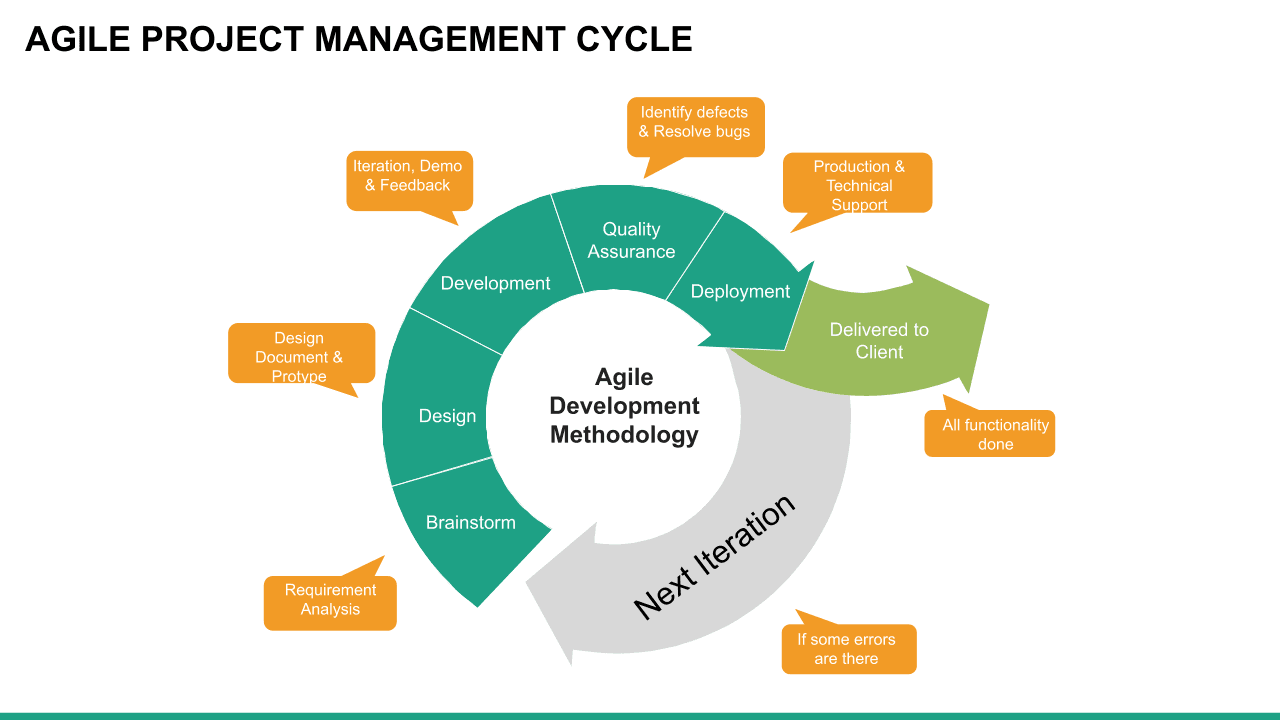
Agile is an approach or philosophy to project management that aims to achieve a goal in small increments. So instead of having one large reveal or launch, an Agile project comprises smaller chunks of tasks that can be continuously delivered in shorter time frames. This makes it easier for project teams to adapt to changing priorities, respond to problems that arise, and cut down on cost, time, and inefficiencies.
6 Popular Agile Certifications
https://www.atlassian.com/agile
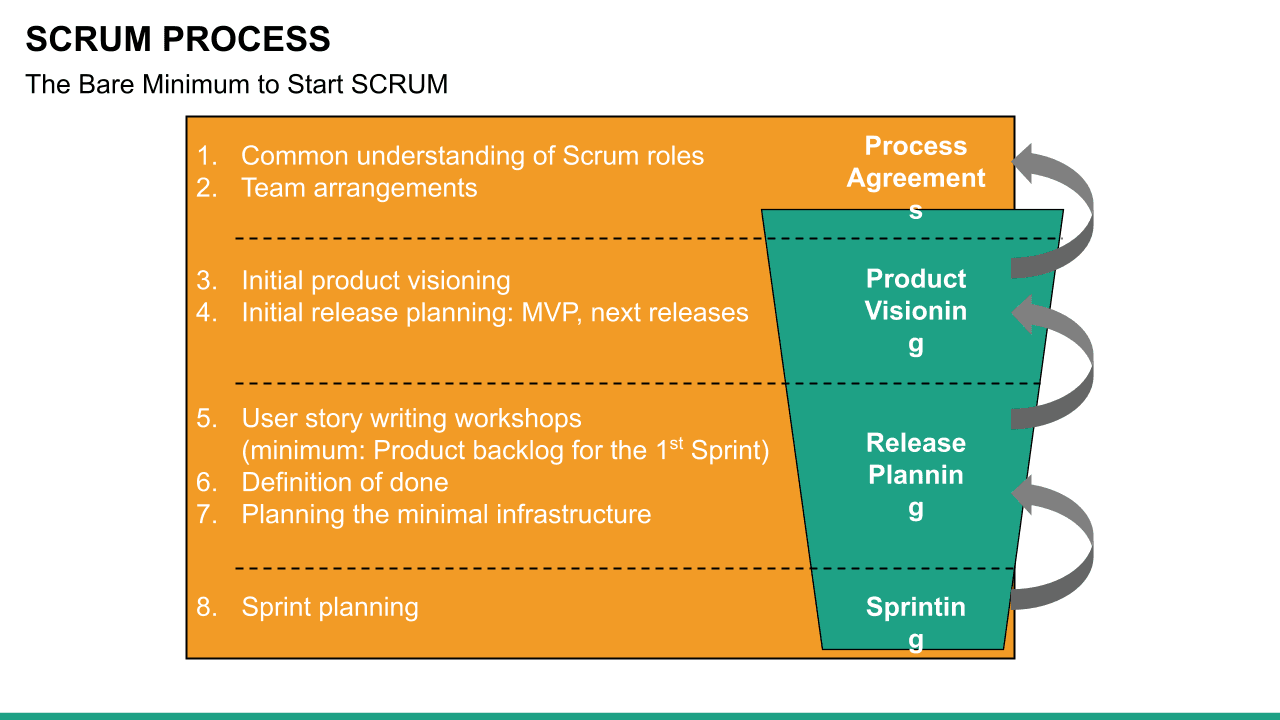
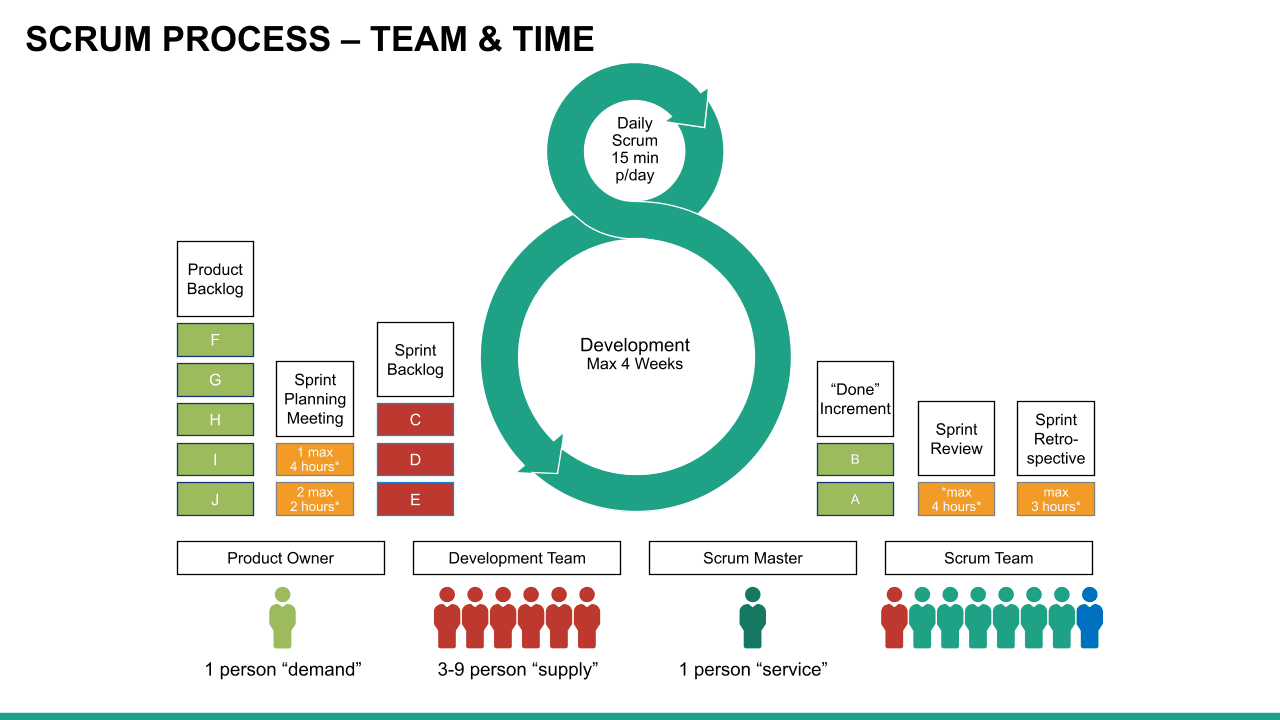
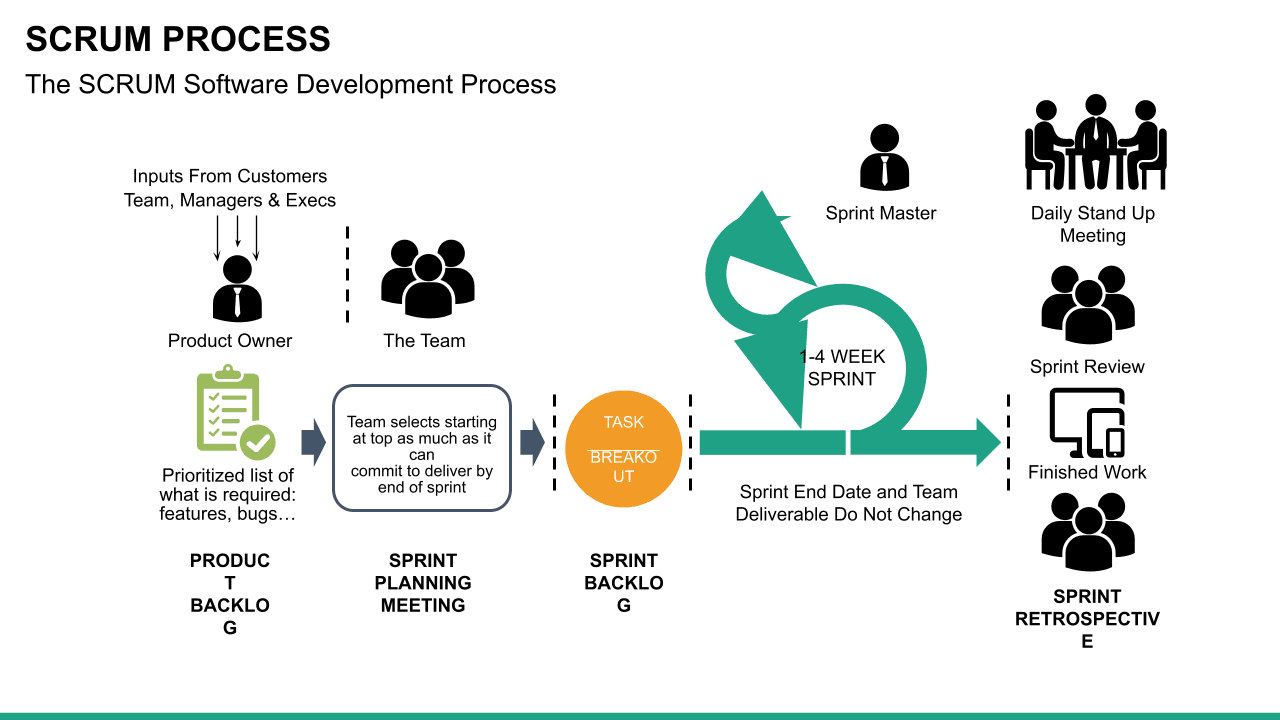
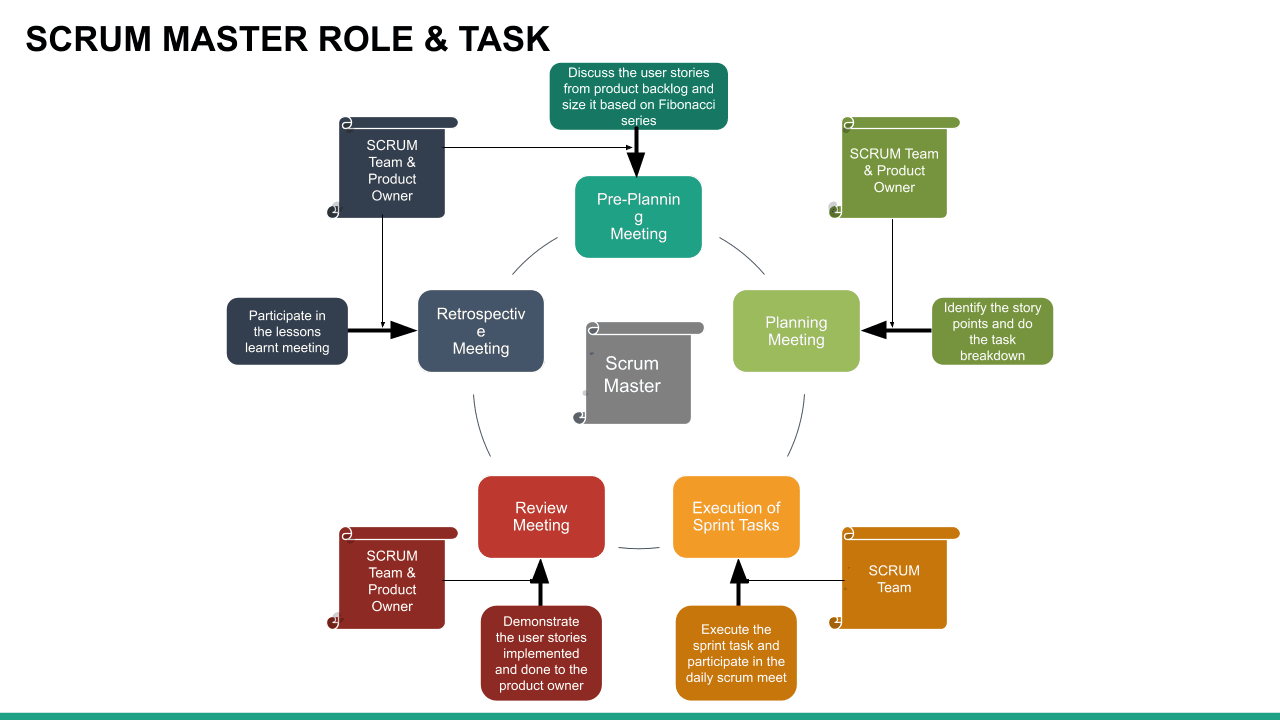
What is Scrum?
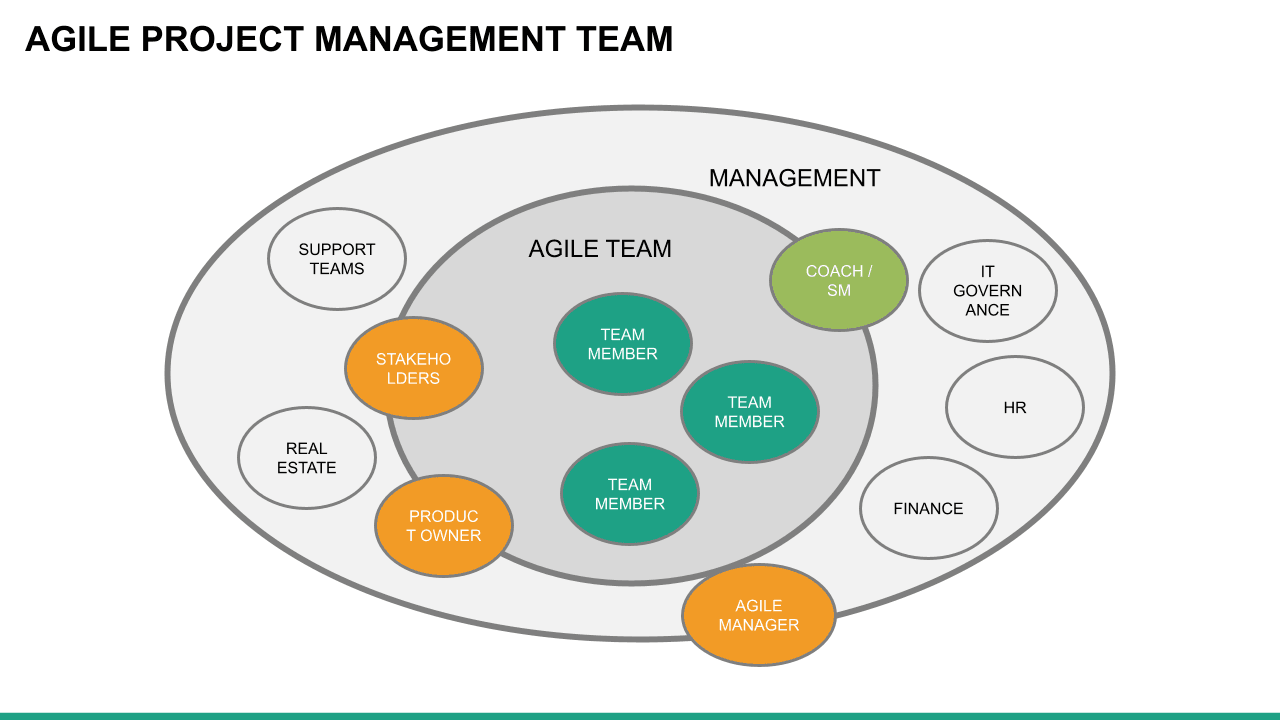
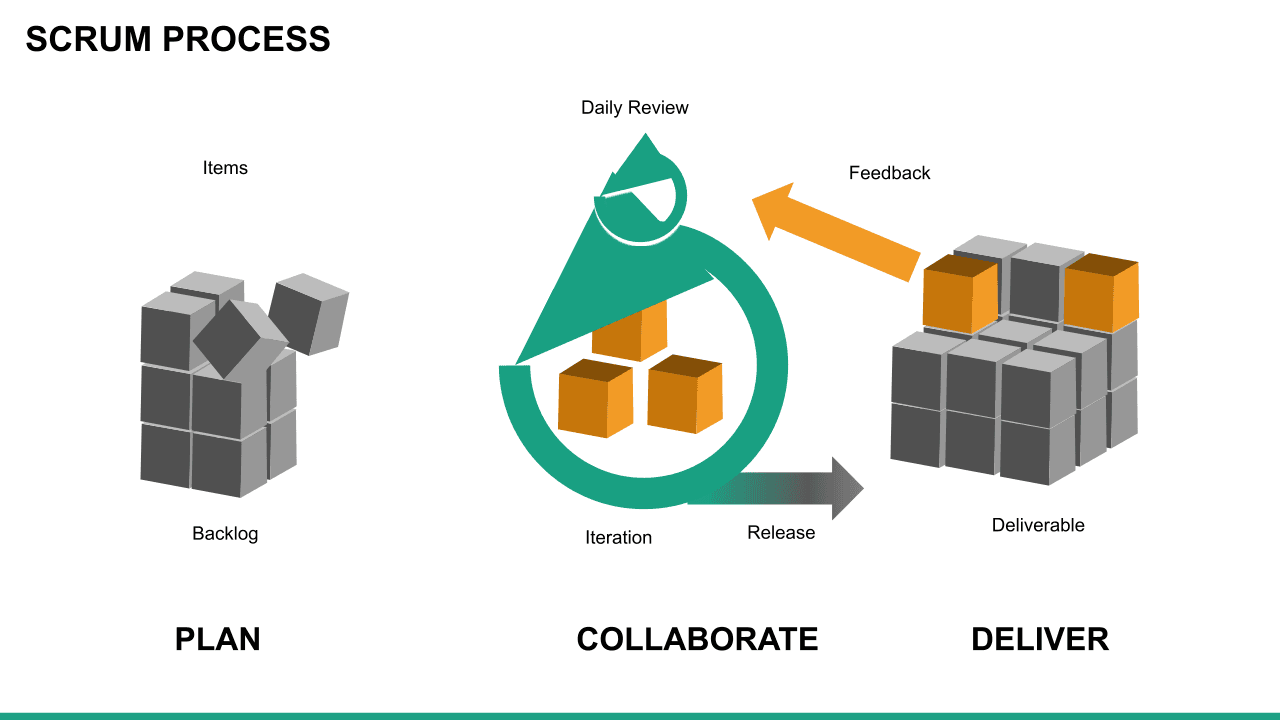
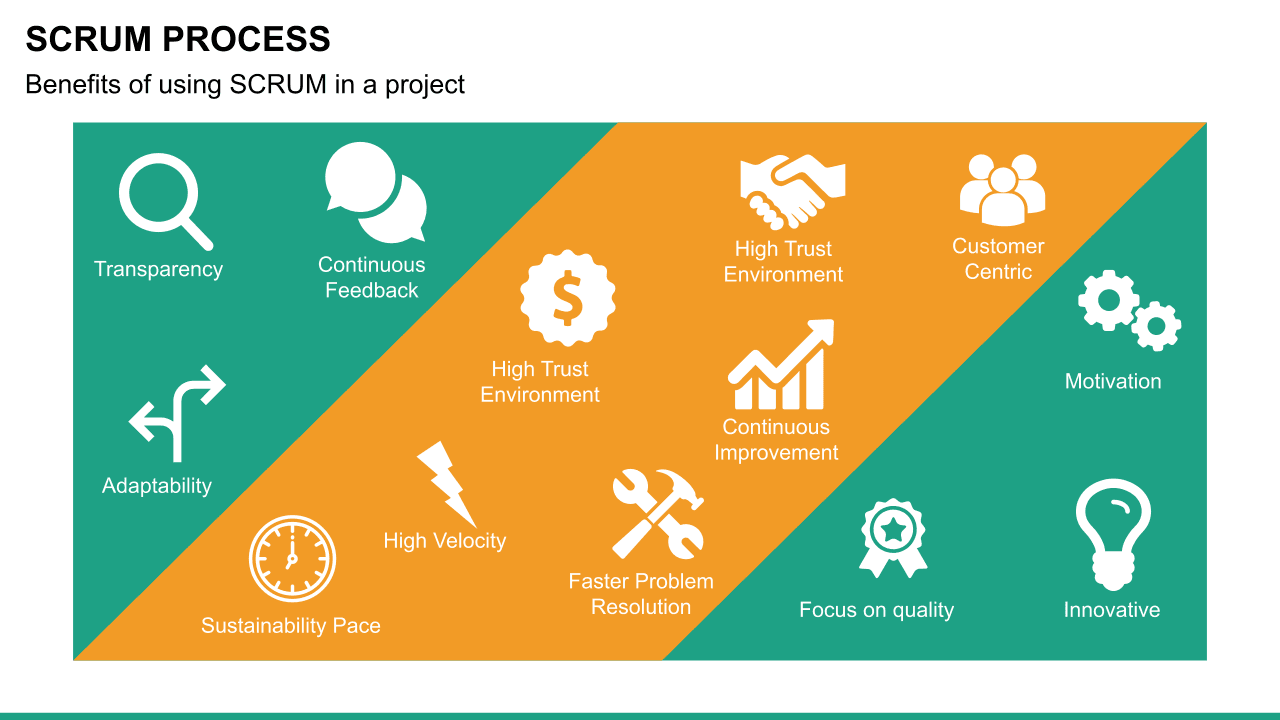
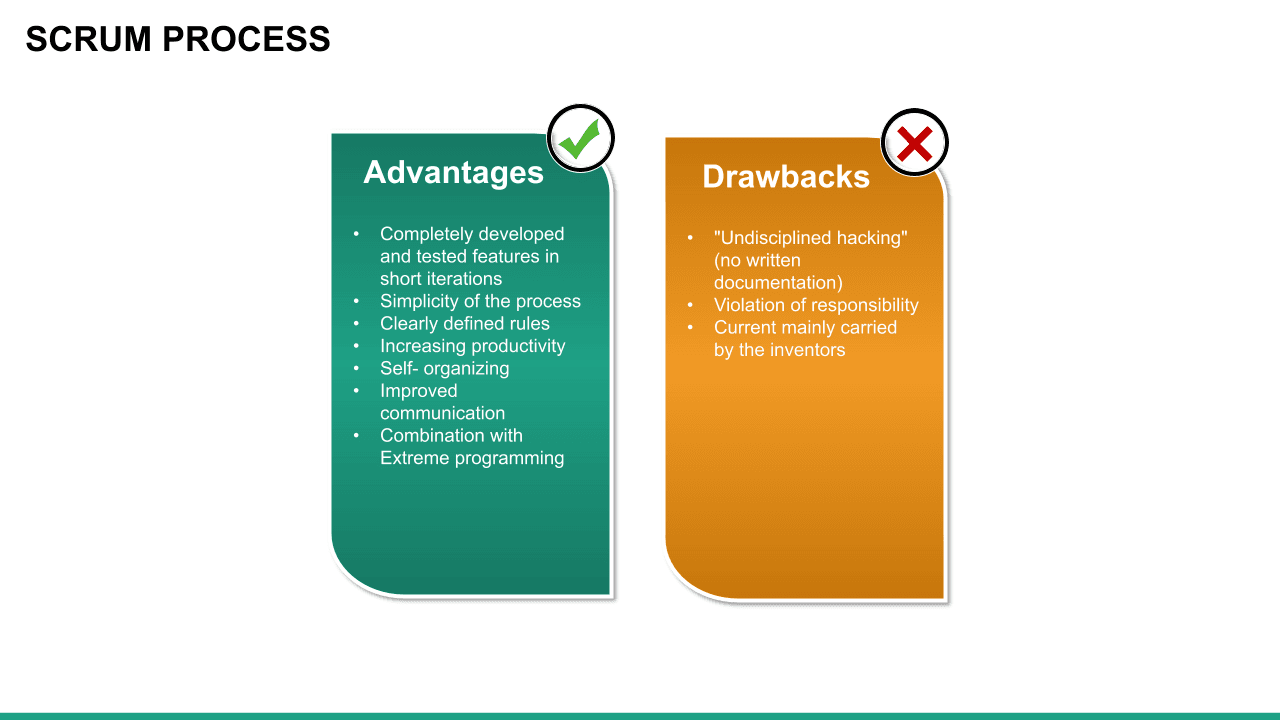
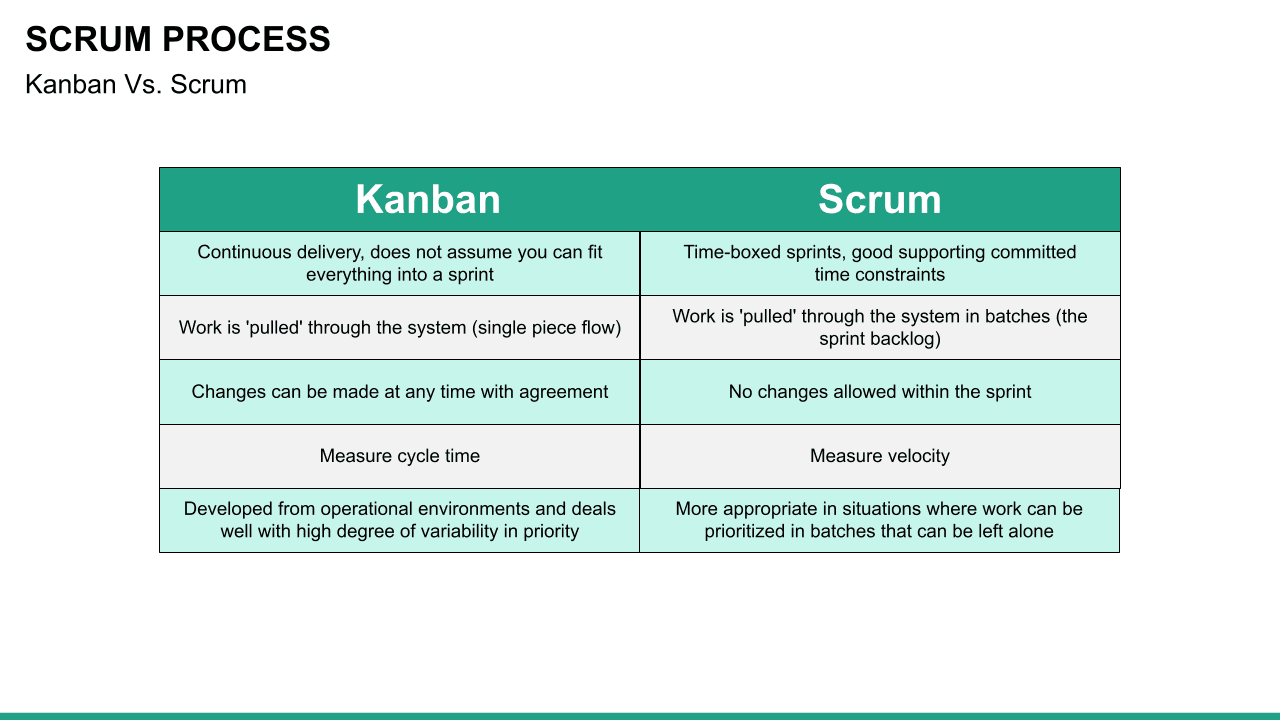
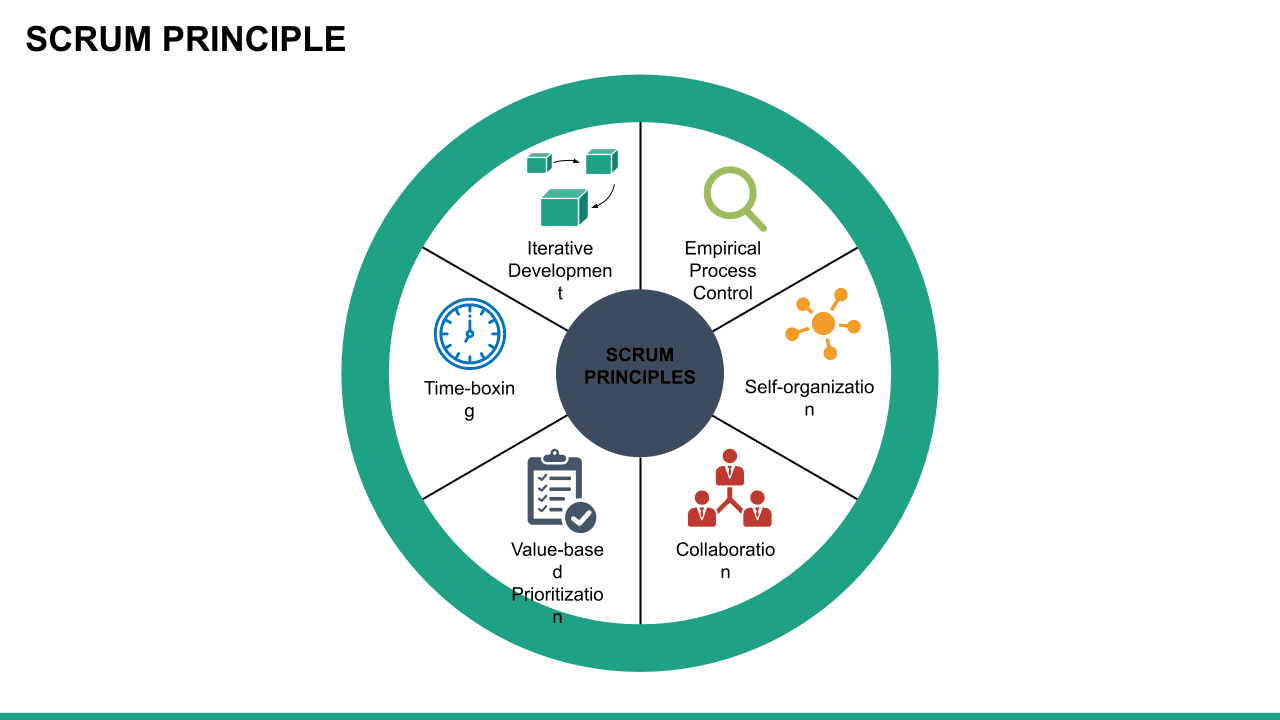
Scrum is an Agile methodology designed to develop products in an environment susceptible to change.
In Scrum, delivery cycles are called “sprints, " generally lasting one to four weeks. Work is incremental and builds on previous work. Scrum teams are usually small, typically three to nine people, and include a Scrum master and a product owner. Communication with team members and stakeholders is consistent, so feedback is constant and changes can be made accordingly.
Scrum Courses & Certifications
JIRA & Confluence
JIRA
Jira is a suite of agile work management solutions that powers collaboration across all teams, from concept to customer, empowering you to do your life's best work together. Jira offers several products and deployment options that are purpose-built for Software, IT, Business, and Ops teams.
Confluence
Create, collaborate, and organise all your work in one place. Confluence is a team workspace where knowledge and collaboration meet. Dynamic pages allow your team to create, capture, and collaborate on any project or idea. Spaces help your team structure, organise, and share work so that every team member has visibility into institutional knowledge and access to the information they need to do their best work.
User Stories
What is a User Story?
User Stories are one of the core elements of the Agile methodology. However, they’re often jumbled with software requirements which isn’t true. So what is a User Story?
A user Story is a small (actually, the smallest) piece of work that represents some value to an end user and can be delivered during a sprint.
The main aim of this element is to put end users in the center of conversation and capture product functionality from their perspective. Thus, developers get a better understanding of what, for whom and why they’re building.
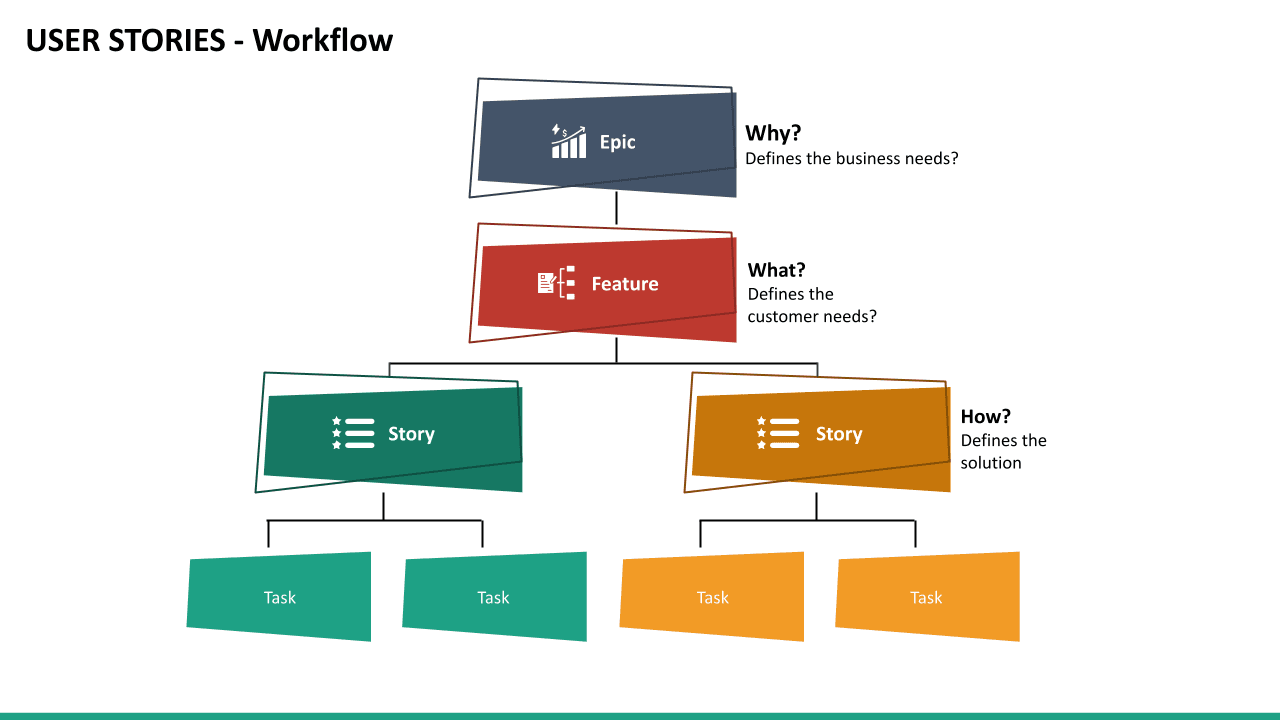
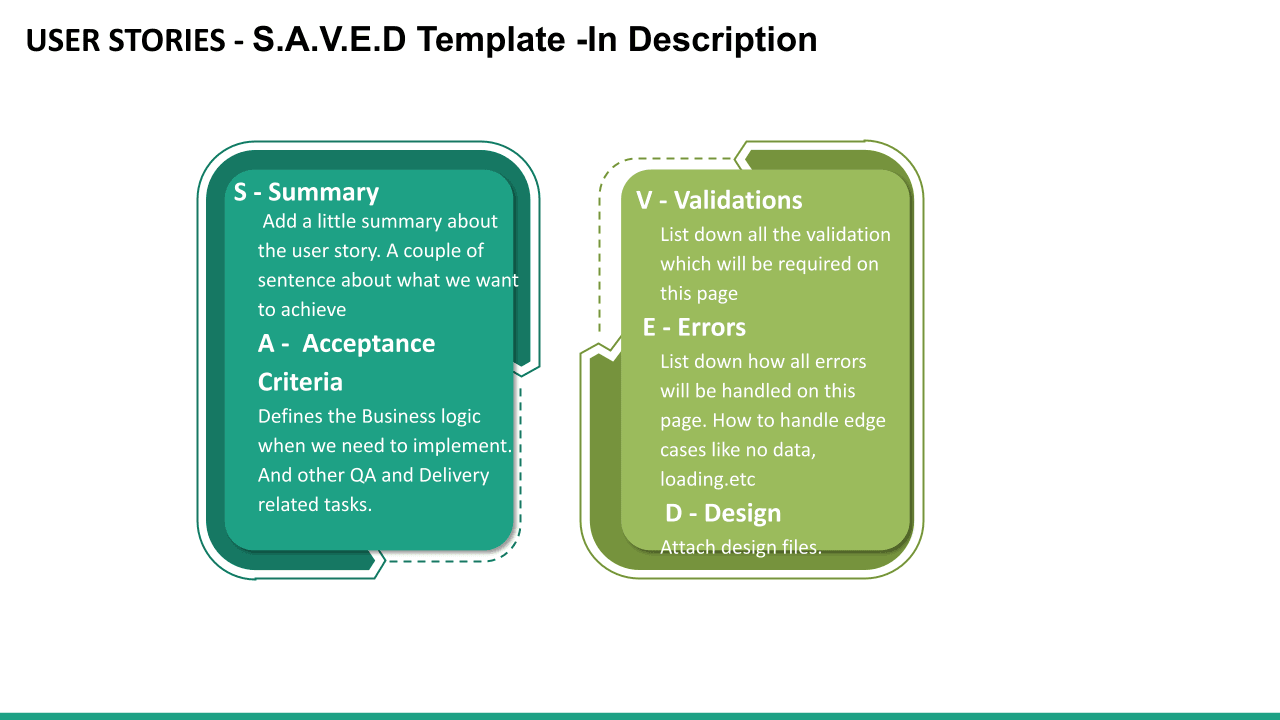

https://www.atlassian.com/agile/project-management/user-stories
User Stories Estimations
You’d most likely start with a product roadmap and a big chunk of work — a scrum epic to be spread across multiple sprints and maybe teams. An epic is a high-level description of the requirements, which you can divide into smaller user stories over several iterations.
In agile development, a user story is the smallest unit of work. It’s a general, often informal, description of software functionality through the lens of the end-user. It helps software teams articulate how a feature delivers value to the customer.
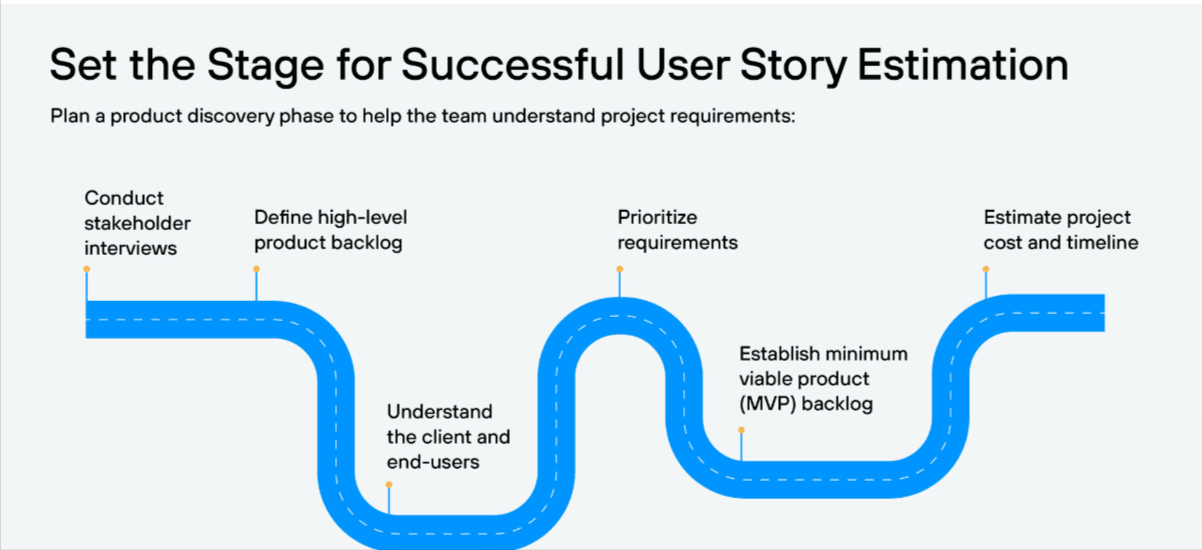
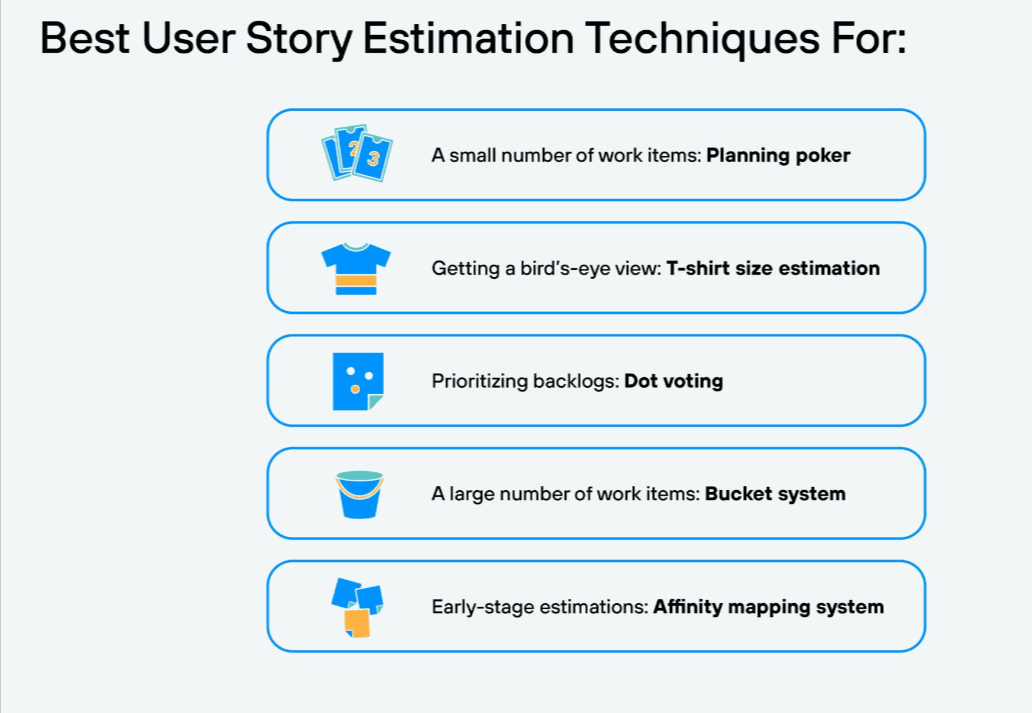
https://www.netsolutions.com/insights/how-to-estimate-projects-in-agile/
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GnG6RPSRLCs
Project Manager - Hard Skills
Hard Skill to the skills you can measure using metrics. Some essential hard skills for a project manager are
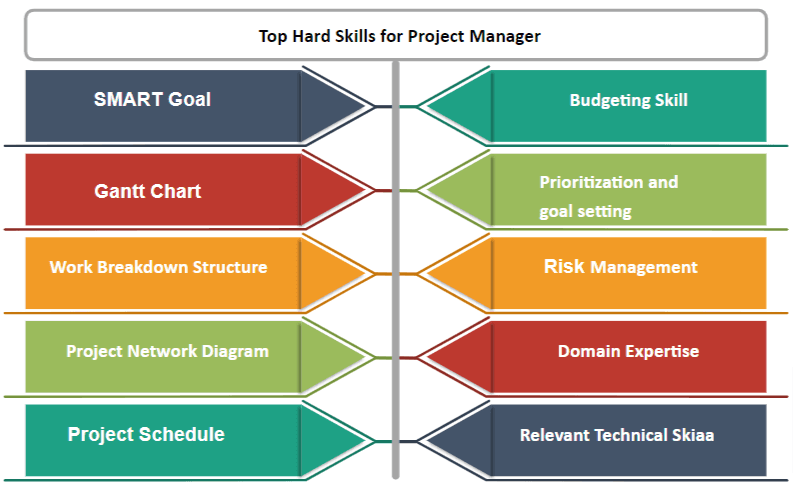
Planning skills:
Accurately estimating time and efforts are the key activities of any project. For a smaller project, this can be done by the project manager itself, but for bigger projects, it is usually done by a planner or scheduler. However, the project manager must validate and review the project schedule. Identifying & integrating various functions and required resources are critical for any project.
- SMART Goal
- SMART is a criterion for setting goals and objectives for projects. According to SMART, your project goals should be Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant and Time-bound.
- GanttChart:
- Gantt charts are one of the most important project management tools due to their versatility. Gantt charts can be used throughout the various phases of your projects to help with project planning, project scheduling and project tracking.
Gantt charts
- Work Breakdown Structure
- The WBS is a graphic representation of every task in the project. At the top is the final product with a line that goes down the page to a box (or boxes) representing the larger tasks leading to that completed project. Each box is then attached to smaller tasks with lines that go under it.
Guide to WBS
**Create a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)**
- Project Network diagram
A network diagram allows a project manager to track each project element and quickly share its status with others. Its other benefits include
- Visual representation of progress for stakeholders
- Establishing project workflows
- Tracking dependencies and potential bottlenecks
Project Network diagram Tools and Techniques
- Project Schedule
Project scheduling involves creating a document, these days usually a digital document, that details the project timeline and the organisational resources required to complete each task.
- Budgeting skills:
Projects are generally bounded by time and budget constraints. The Project Manager should have sufficient skills to allocate the budget based on project cost estimates. Every WBS of a project requires some budget allocation to complete the work, and project managers are responsible for ensuring the project remains within its allocated budget.
- Prioritization and goal setting
There are a seemingly endless number of tasks that go into doing any project, but not all of them can happen at the same time. It’s on the PM to determine what is the highest priority and what can wait until later. The PM needs to make priorities clear to team members and connect them to tangible team goals.
- Risk Management:
Projects are continuously exposed to various schedule and cost risks. Managing these risks is the responsibility of the project manager. It’s not just about managing people and resources. Identifying risks and mitigating those risks by the project team should be acted upon daily.
- Project Data Analytics:
As the project progress, it continuously generates key information and data about project performance. The Project Manager should be able to measure and analyse these data & key performance indicators (KPIs). This helps the Project manager to make informed and effective decisions. Project managers need to understand and analyse this data for ongoing project work and plans.
- Domain Expertise:
To effectively manage a project, project managers must be proficient in industry-specific knowledge. For an IT project manager, it is critical to have a clear understanding of the software industry and coding knowledge. Similar to construction projects, a civil engineer will have a better understanding of construction work. It is very difficult to manage a project if you know little or nothing about the specific industry.
- Relevenet Technical Skills:
While the exact skills we refer to will vary from project to project, a good PM must have a solid background in their team is work. For example, if you are managing a development team making an app, having at least some basic technical skills and background knowledge is beneficial. Some examples are given below:
- Deployment process Understanding Application Deployment
- Source code management - Git/GitLab
- App submission process on Apple or Google play store
- AWS
Project Manager Soft Skills
Soft skill is a personal attribute that supports situational awareness and enhances an individual’s ability to complete the project. The term soft skills are often used as a synonym for people skills or emotional intelligence**.**
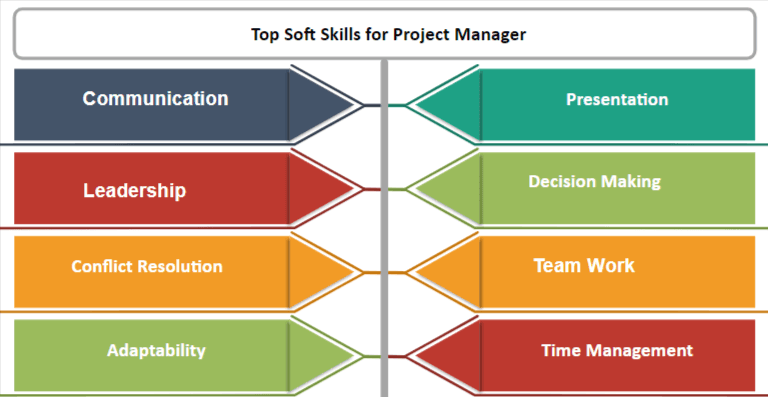
- Presentation Skills:
Presentation skills are needed for delivering effective and informative presentations to the stakeholders. These skills require knowledge of various areas such as the structure of your production, data regarding project schedule, lookahead plan, budget status, risks, and mitigation plans.
Presentation skills are critical to conveying the project status and correct information to stakeholders and business leaders. Learning to design presentations that will hold people’s attention and present project status and risks in an understandable format is vital for getting everyone on board.
Courses to learn
Presentation Skills
- Communication Skills:
Communication skills are the abilities you use when giving and receiving different kinds of information. The ability to communicate clearly and effectively is an essential skill for project managers. Project managers use various tools and platforms to communicate with project teams, outside subcontractors, key stakeholders, and sponsors. In addition to the basics like speaking and writing, effective communication also includes understanding and identifying general sentiments and nonverbal cues like body language and tone of voice. This helps the project managers to determine the sign of trouble among team members and things get out of control.
- Leadership Skills:
Project managers must use their leadership skills to communicate clearly and effectively, inspire, influence, motivate, and build a consensus among their team—primarily through periods of high stress. These include strategic thinking, planning and delivery, people management, change management, communication, persuasion, and influence.
Leadership Learnings
- Decision-Making Skills:
The Project Manager must create clarity out of ambiguity. They must evaluate risks and opportunities and commit to achieving their goals. Also the project manager must also ensure that their decisions maintain the company vision and business goals. The project manager usually faces high pressure, complex circumstances, opportunity deadlines, too much or too little, or conflicting information throughout the project. Decision-making in difficult situations is always challenging in a projectized organisation.
Decision-Making
- Conflict Resolution:
Conflict is a normal part of any project. After, stakeholders can’t be expected to always agree on everything. There are bound to be situations when tensions flare, and conflicts arise throughout a project. This can happen between members of the team or clients or stakeholders, or between management leaders. A project manager must be skilled at navigating these situations and defusing tensions for the good of the group, stakeholders, and project. When mismanaged, conflict can cause significant harm to a client’s (internal and external) relationship. Still, when handled respectfully and positively, conflict provides an opportunity to strengthen the bond between team members.
Conflict Resolution
- Teamwork
Everyone on your team has something to bring to the table, and your team is more effective working together than they would be alone. Teamwork ensures that everyone feels welcome and valued and supported to contribute.
If you’re working to boost your teamwork skills, dig deeper into team brainstorms and 1:1 conversations, and ask for feedback from your team—how can you be a better team member? Notice if there’s someone who hasn’t spoken up in a while, and be supportive when another team member has a new idea.
- Adaptability At some point, aspects of your project plan will change, whether it’s this project or the next one. Maybe your deadline or priorities shifts, and you need to adapt your workflow accordingly. Great project managers can pivot and adapt to new situations to continue steering their project team in the right direction.
- Time management Time management and organisation skills go hand in hand. As you improve at organising your tasks, you’ll also have a clearer sense of everything on your plate and how long your upcoming tasks will take. Time Management
Quality Management
Quality management is the act of overseeing all activities and tasks needed to maintain a desired level of excellence. The project manager should make sure that all stakeholders in a business work together to improve processes, products, services and the culture of the company itself.
Quality management includes determining a quality policy, creating and implementing quality planning and assurance, and quality control and improvement.
- Quality Assurance Project Manager Helps Streamline the project Quality Quality Assurance Process. He/she should be aware of the overall quality management and process it involves. Quality assurance is used in project management to help companies avoid mistakes and minimize potential risks. With quality assurance in mind, project managers can start planning for the quality of their deliverables from the very beginning of their project plans.
Types of Quality Assurance Methods
- Statistical process control
- Failure testing
- Total quality management
- Quality Control Quality control is a process that involves inspecting, testing, and reporting outputs to ensure that they meet the requirements of the project. To achieve the highest possible level of conformance, decisions need to be made in all phases of quality control. The project Manager should be aware of all tools, techniques and processes followed during the complete QA cycle.
QA Porcess
QC & QA In Project Management
That’s it for today
I hope the Learning Path helps you level up your skills in the project Management.
