- Published on
Crownstack's QA Process
- Authors
- Written by :
- Name
- Neha Arora
What is QA Process?
First of all, let's understand What is Process? A process is something that gives results in a defined manner. To get good/productive results in any field one needs to follow the defined process. Similarly, for the QA department, we decided to create a “Process” following which we get efficient results.
Importance of Process
For any organization setting up processes and following them at the same time is very important and beneficial too. Especially for a start-up to set up a process from the scratch is very crucial. They are important because how they are done determines how successful the outcomes will be. If you focus on the right processes, in the right way, you can design your way to success.
Quality assurance (QA) processes play a crucial role in ensuring the quality of software products and meeting the requirements of customers. Here's how QA processes help in various areas.

- Meets customer requirements: QA processes help to validate the software against the customer requirements. This includes functional testing, regression testing, and user acceptance testing, ensuring that the software meets the customer's needs and expectations
- Saves money and time:: By catching defects early in the development process, QA processes help to avoid costly and time-consuming rework. This can also reduce the likelihood of delays in a software release
- Improves customer satisfaction: QA processes help to ensure that the software is of high quality and performs as expected, leading to higher customer satisfaction
- Compliance with industry standards: QA processes help to ensure that the software complies with relevant industry standards and regulations
- Improves communication and collaboration: QA processes involve collaboration between various teams, including developers, testers, and stakeholders. This collaboration helps to improve communication and ensure that everyone is on the same page, leading to a more efficient development process
Challenges to Implement Processes
We often face a unique set of challenges when implementing QA processes due to limited resources, tight budgets, and fast-paced development cycles. However, by implementing cost-effective and efficient QA processes, startups can overcome these challenges and ensure that their products meet the desired level of quality.
Some unique challenges we (startups) face when implementing QA processes include.

- Limited Resources: Startups typically have limited resources and are often forced to do more with less. This can make it challenging to allocate the necessary resources for implementing a comprehensive QA process
- Tight Budgets: Startups typically operate on tight budgets and need to make every penny count. As a result, investing in a comprehensive QA process can be difficult, especially when there are other areas of the business that also need funding
- Fast-Paced Development Cycles: Startups often operate on a tight timeline and need to get their products to market quickly. This can make it challenging to implement a comprehensive QA process that can slow down the development cycle
We at Crownstack have implemented the QA process keeping the above challenges in mind and to overcome those find out the below practices.
- Keeping Quality on priority: We start the testing from the very early stages of the development and keep quality in every aspect of the product development cycle and this helps us avoid bug fixing and issues later in the cycle
- Follow Agile methodology: Agile helps us achieve quality in a fast-paced development cycle. By breaking down the development cycle into smaller sprints we can test and validate their products at every stage, reducing the risk of critical issues
- Adopt Automated Testing: Automated testing helps reduce the time and cost associated with manual testing and catches issues early in the development cycle
- Use Cloud-Based Tools: Cloud-based QA tools can help startups save on infrastructure costs and allow them to scale their testing efforts as needed. Additionally, these tools often come with a pay-as-you-go pricing model, making them more cost-effective for startups
Stages of the QA Process
Analyze Requirements
QA should be involved in analyzing and defining software requirements, both functional and non-functional. QAs must be offered consistent, comprehensive, traceable requirements and clearly marked. Being in the discussion from scratch helps them understand the requirement well and the changes made in them in later stages. This helps the QA team design test cases tailored explicitly to the software being tested.
Test Plan Designing
Prepare Test Plan (However this is subject to the project requirement (PM/QA Lead decides if this needs to be created). The information gained during the requirements analysis phase is used for test planning. The test plan should comprise the testing strategy, the scope of testing, the project budget, and set deadlines. It should also outline the types and levels of testing required, methods, and tools for tracking bugs and allocate resources and responsibilities to individual testers. It should also include out-of-scope testing and unsupported OS versions and devices.
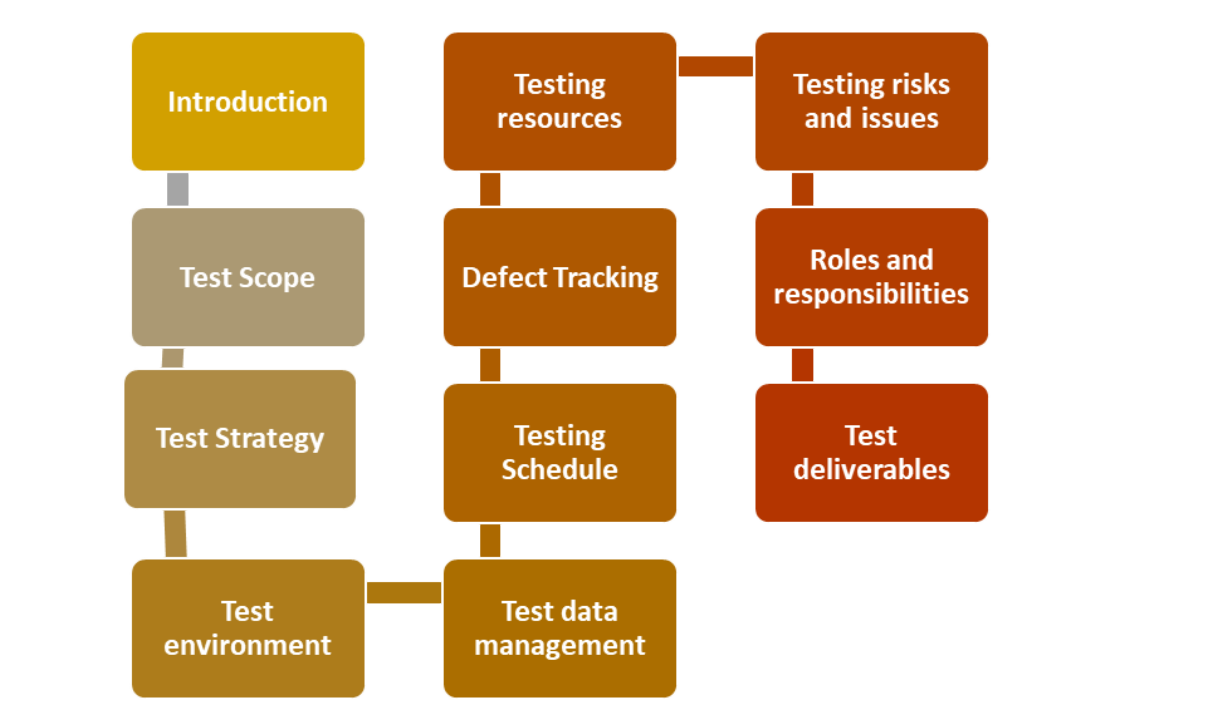
- Introduction: An overview of the software product being tested and the objectives of the test plan
- Test Scope: A description of the scope of the testing, including the features and functionalities to be tested, the testing methods to be used, and any assumptions or limitations
- Testing Strategy: An outline of the testing methodologies to be used, such as manual testing, automated testing, regression testing, or performance testing
- Test Environment: A description of the testing environment, including the hardware and software configurations, and any third-party applications that are required
- Test Schedule: A timeline for the testing activities, including testing phases, milestones, and deadlines
- Defect Tracking: When testing a software product, it's important to keep track of any problems or defects we find and ensure they are fixed
- Test Resources: A list of the resources required for testing, such as personnel, hardware, software, and tools
- Test Data: A description of the test data that will be used during testing, including test data scenarios, input data, and output data
- Test Risks: A description of the potential risks that could impact the testing process and the measures that will be taken to mitigate these risks
- Test Deliverables: A list of the documents and artifacts that will be produced during testing, such as test reports, defect reports, and test logs
To know in-depth how we design a test plan in Crownstack, continue reading: Crownstack's Test Plan Workflow.
Test Case Designing
QA teams must craft test cases and checklists encompassing the software requirements at this stage. Each test case must contain conditions, data, and the steps needed to validate each functionality. Every test must also define the expected test result so testers know what to compare actual results to. All the negative and positive test cases should be covered to achieve maximum test coverage.

- Understand the Requirements: It's important to have a clear understanding of the requirements before writing test cases. This will ensure that the test cases cover all the required features and functionalities
- Use a Standard Format: Use a standard format for writing test cases to make them easy to read and understand. Include the test case ID, the test case name, the test steps, the expected result, and any additional information that is relevant
- Keep Test Cases Short and Simple: Test cases should be short and simple so that they are easy to understand and execute. Each test case should test one specific feature or functionality
- Write Test Cases for Positive and Negative Scenarios: Write test cases for both positive and negative scenarios. Positive scenarios test that the software performs as expected, while negative scenarios test that the software handles errors and exceptions correctly
- Use Clear and Concise Language: Use clear and concise language when writing test cases. Avoid technical jargon and make sure that the test cases are easy to understand for anyone who needs to execute them
- Test Each Input and Output: Test each input and output of the software to ensure that they function correctly. This includes checking for valid inputs and expected outputs, as well as invalid inputs and unexpected outputs
- Include Preconditions and Postconditions: Include any pre-conditions and postconditions that are necessary for executing the test cases. This will ensure that the test cases are executed correctly and consistently
- Review and Validate Test Cases: Review and validate the test cases before executing them. This will ensure that they are accurate, complete, and effective in testing the software
At Crownstack, we use our in-house product “Bugplot” (https://www.bugplot.com) for test case writing and test execution as well. After text execution, it generates a detailed test report also which can be shared with anyone.
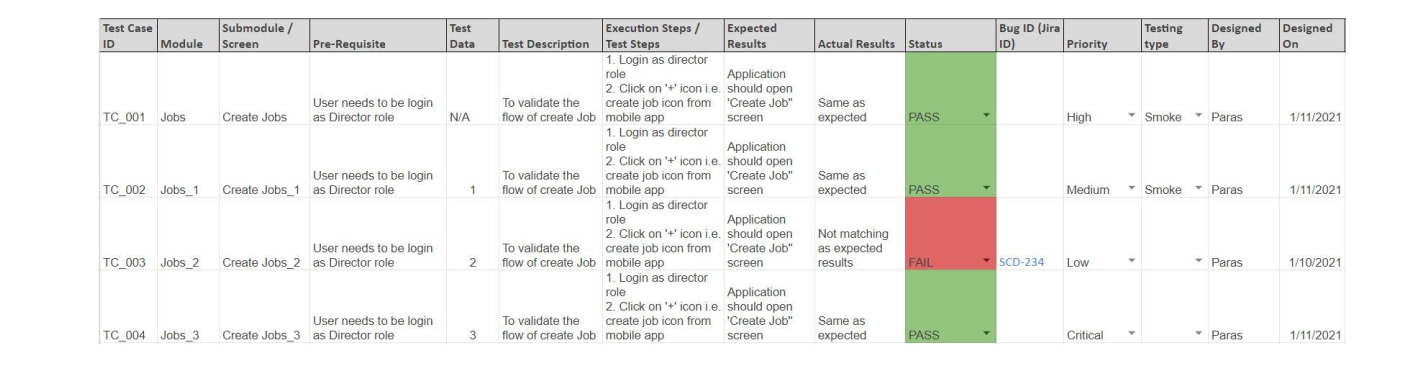
A Template of the test case: we follow the below template if any client prefers a spreadsheet to manage test cases.
Execute Tests and Report Defects
In this phase, the QA team executes the test cases and reports any defects or issues that they find. Manual test cases are run in accordance with previously designed test cases. All bugs detected are submitted in a defect tracking system for effective defective management. Additionally, test automation engineers can use an automated test framework such as Selenium, Cypress, or Appium to execute test scripts and generate test reports.
When reporting a bug, it's important to provide as much detail as possible to help developers reproduce and address the issue. Here are some steps to follow:
- Provide a clear and descriptive title for the bug report that summarizes the issue
- Describe the problem in detail, including any error messages or unexpected behavior that you've observed. Be specific about the steps you took that led to the problem, and include any relevant context, such as the operating system or device you're using
- Include screenshots or videos if possible, as these can be helpful in illustrating the issue
- If you're reporting a bug in the software, including information about the version number you're using and any relevant system information, such as the operating system and hardware specifications
- If you've identified a possible cause for the problem or a workaround that you've used, include that information as well
- Be respectful and constructive in your communication with the developers, and provide feedback that is helpful in improving the product
For Bug reporting, we use Jira and below is the guideline/format to log bugs in it : Bug Reporting Template.
Test Reporting
The QA team creates a report summarizing the testing results, including the number of tests executed, defects found, and their severity.
We have a defined format for test reports here at Crownstack - Sample Test Report.
Retesting and Regression testing
After the defects are fixed, the QA team retests the affected functionality to ensure that the fixes did not introduce new issues. They also perform regression testing to ensure that the fixes did not affect other parts of the project. The regression testing could be executed manually or by executing the automated regression test suite depending on the project's need.
Sign off
Once the testing is complete and all defects have been resolved, the QA team signs off on the project with signs off report and approves it for release. A QA sign-off report is a document that confirms that a project or product has met the required quality standards and is ready for release. The contents of a QA sign-off report may vary depending on the project and organization but generally include:
- Summary: A brief overview of the project's purpose and objectives
- Scope: A description of the scope of the project and the features that were tested
- Testing Process: A summary of the testing process, including the testing methodologies, tools used, and test results
- Issues and Defects: A list of any issues and defects found during testing, along with their severity and resolution status
- Test Coverage: A summary of the test coverage, including the percentage of requirements tested and the number of test cases executed
- Acceptance Criteria: Confirm that the project has met all the acceptance criteria specified in the requirements
- Release Recommendation: A recommendation for the release of the project, along with any required actions or conditions for release
- Sign-off: The QA team's sign-off indicates that the project has met the required quality standards and is ready for release
We have defined a format for the same and we called it BCR at Crownstack(Build Completion Report) BCR Format.
Outcomes
Implementing a QA (Quality Assurance) process can have several positive outcomes for an organization, some of which are:
- Make the process of creating a product more efficient by identifying areas that can be improved or eliminated to save time and resources
- Reduce the risk of errors and defects in the product by catching them early in the development process, which can save money and prevent negative impacts on customers
- Improve communication and teamwork among team members to make sure everyone is working together towards the same goal
- Make customers happier by creating products that better meet their needs and expectations
- Use data collected during the QA process to make better decisions and continuously improve the product
- Ensure the product meets industry standards and complies with regulations to avoid legal or financial problems
Overall, implementing a QA process can help organizations improve their processes, reduce the risk of errors and defects, enhance communication and collaboration, increase customer satisfaction, make better decisions, and ensure compliance with standards and regulations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a strong Quality Assurance (QA) process is essential to ensuring the quality and reliability of software products. This blog has explored the key aspects of a comprehensive QA process, including test planning, test execution, defect management, and reporting. We have also highlighted the importance of continuous improvement and provided resources and tools to help organizations implement effective QA processes.
As software development becomes increasingly complex, QA becomes even more critical to ensure customer satisfaction, reduce rework, and increase productivity. Therefore, it is important for individuals and organizations to prioritize the implementation and continuous improvement of QA processes.
You can begin practicing the QA process by creating/working on the below items:
- Start by creating a basic QA plan for their software development process
- Implement an automated testing framework to save time and effort
- Identify and prioritize critical areas for testing
- Use agile development methodologies to incorporate QA testing into each iteration
- Seek out QA training and certifications to improve skills and knowledge
We encourage our readers to consider implementing these best practices in their own work or organization and to share this information with others in the software development community. By prioritizing QA, we can deliver high-quality software products that meet users' needs and drive business success.
