- Authors
- Written by :
- Name
- Divanshu Gupta
Getting Started with JMeter: A Beginners Guide
- Published on
- Published On:
Introduction to Apache JMeter
Apache JMeter is a powerful open-source tool designed for load testing, performance testing, regression testing, and functional testing across different protocols and technologies.
Being a Java-based desktop application, JMeter comes with a graphical interface built using the Swing API, making it platform-independent. This means you can run it on Windows, Linux, macOS, or any system that supports a Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
Protocols Supported by JMeter
JMeter is not limited to web applications—it supports a wide range of protocols and services:
- Web Applications: HTTP, HTTPS (Web 1.0 and Web 2.0 technologies like Ajax, Flex, AMF)
- Web Services: SOAP, XML-RPC
- Databases: JDBC connections
- Directory Services: LDAP
- Messaging Services: JMS
- Mail Servers: POP3, IMAP, SMTP
- File Transfer: FTP
How JMeter Works?
JMeter simulates a group of users sending requests to a target server, and returns statistics that show the performance/functionality of the target server/application via tables, graphs, etc.
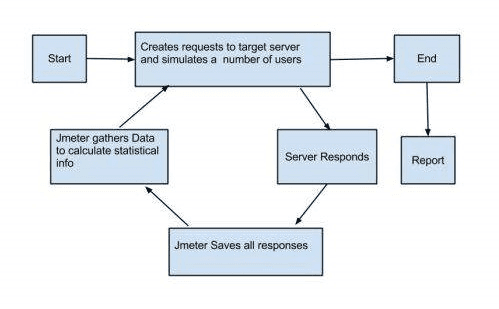
Flow of JMeter Working
- Start
- The test begins with a Test Plan execution.
- Creates Requests & Simulates Users
- JMeter (via Thread Groups) creates multiple virtual users.
- These users send requests (HTTP, FTP, JDBC, SOAP, REST, etc.) to the target server/application.
- Server Responds
- The target server processes the requests and sends back responses.
- JMeter Saves Responses
- JMeter stores all responses (can be in memory or disk depending on listener/config).
- These responses can be validated using Assertions.
- JMeter Gathers Data
- It collects performance metrics such as:
- Response time
- Throughput
- Latency
- Error %
- Transactions per second
- This data is used for statistical analysis.
- It collects performance metrics such as:
- Report Generation
- Based on the collected data, JMeter generates tables, graphs, and dashboards.
- End
- Once execution is complete, results are saved and available for review.
What is a Test Plan in JMeter?
A Test Plan is the backbone of any JMeter test. Think of it as a container that defines what to test and how the test should run.
A Test Plan is made up of multiple components such as Thread Groups, Controllers, Listeners, Timers, Assertions, and Configuration Elements. Importantly, every test plan must include at least one Thread Group.
Types of Testing We can Perform Using Jmeter
- Performance Testing
- Checks the responsiveness, throughput, reliability, and scalability of an application under load.
- Examples: Stress test, spike test, endurance test.
- Load Testing
- Simulates expected user traffic to see how the system behaves under normal and peak load conditions.
- Stress Testing
- Tests the system beyond its maximum load to find breaking points.
- Functional Testing
- JMeter can also verify functional correctness of APIs or web applications using assertions.
- API / Web Services Testing
- Supports REST, SOAP, and other service calls with request/response validation.
Core Elements of a JMeter Test Plan
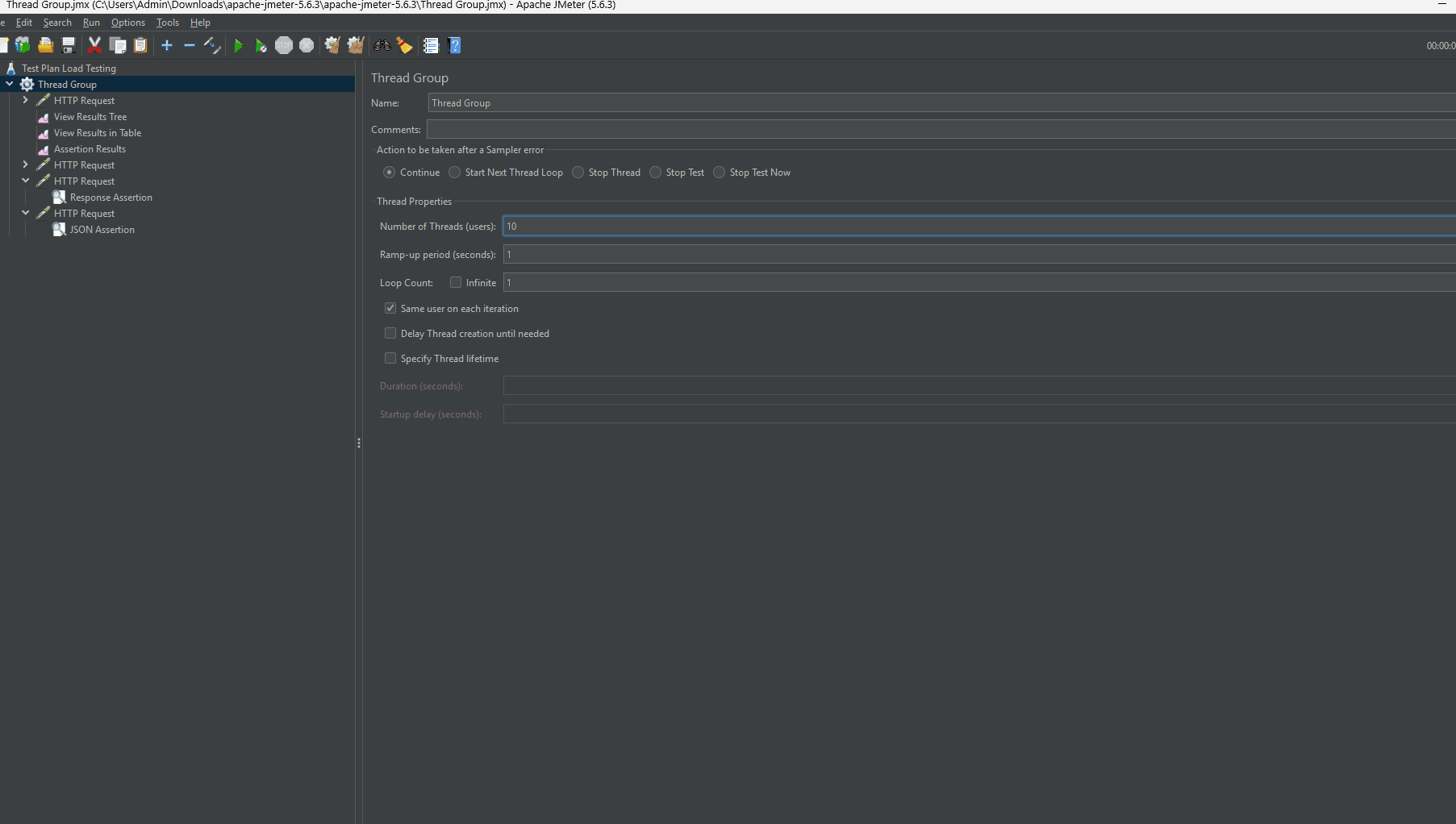
1. Thread Group
Represents a group of users (virtual threads) performing tasks.
Defines the number of users, ramp-up period, and iteration count.
2. Controllers
Controllers decide how requests are sent. JMeter has two types:
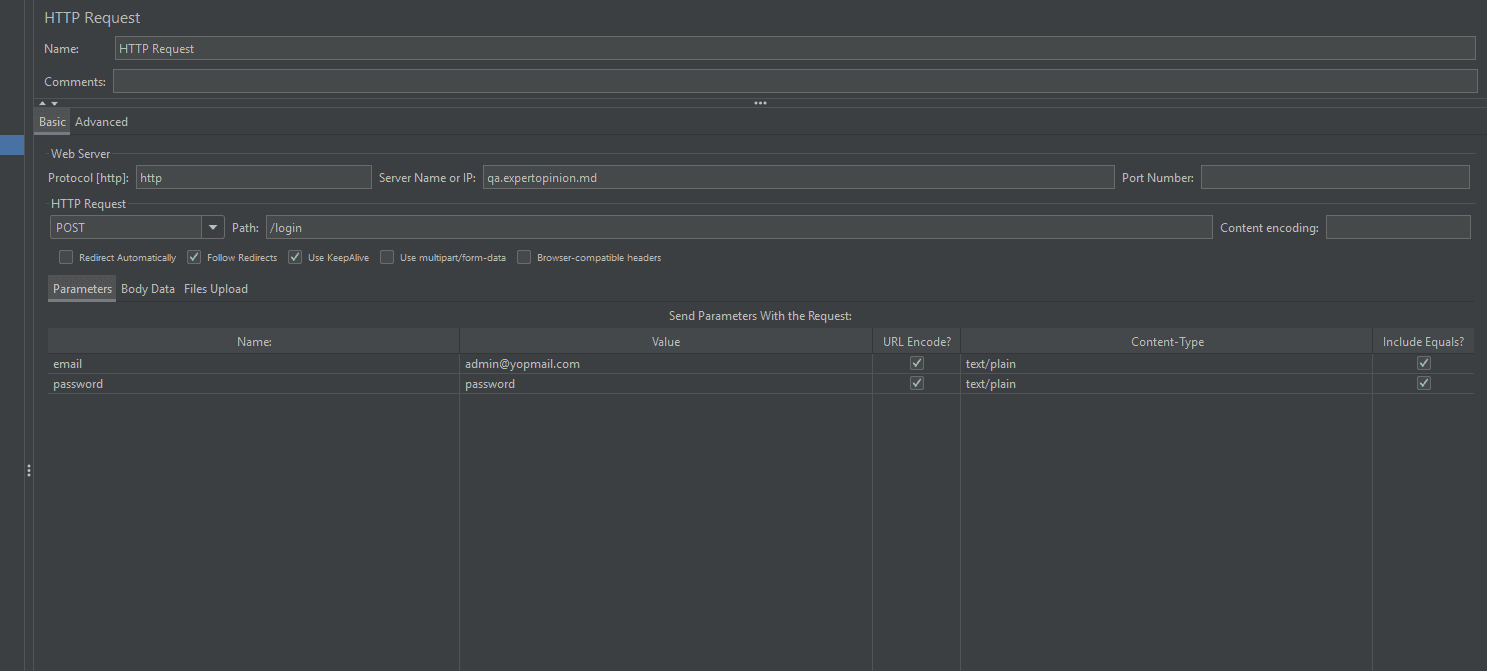
Samplers: Used to send requests to the server. For example, anHTTP Request Sampler can simulate GET, POST, or DELETE requests.
Logic Controllers: Define the order and logic of request execution.
3. Listeners
Listeners capture and display test results. They help you visualize performance data in various formats:
View Results Tree
View Results in Table
Aggregate Report
Graph Results
Summary Report
Simple Data Writer
Assertion Results
Distribution Graph (alpha)
Aggregate Graph
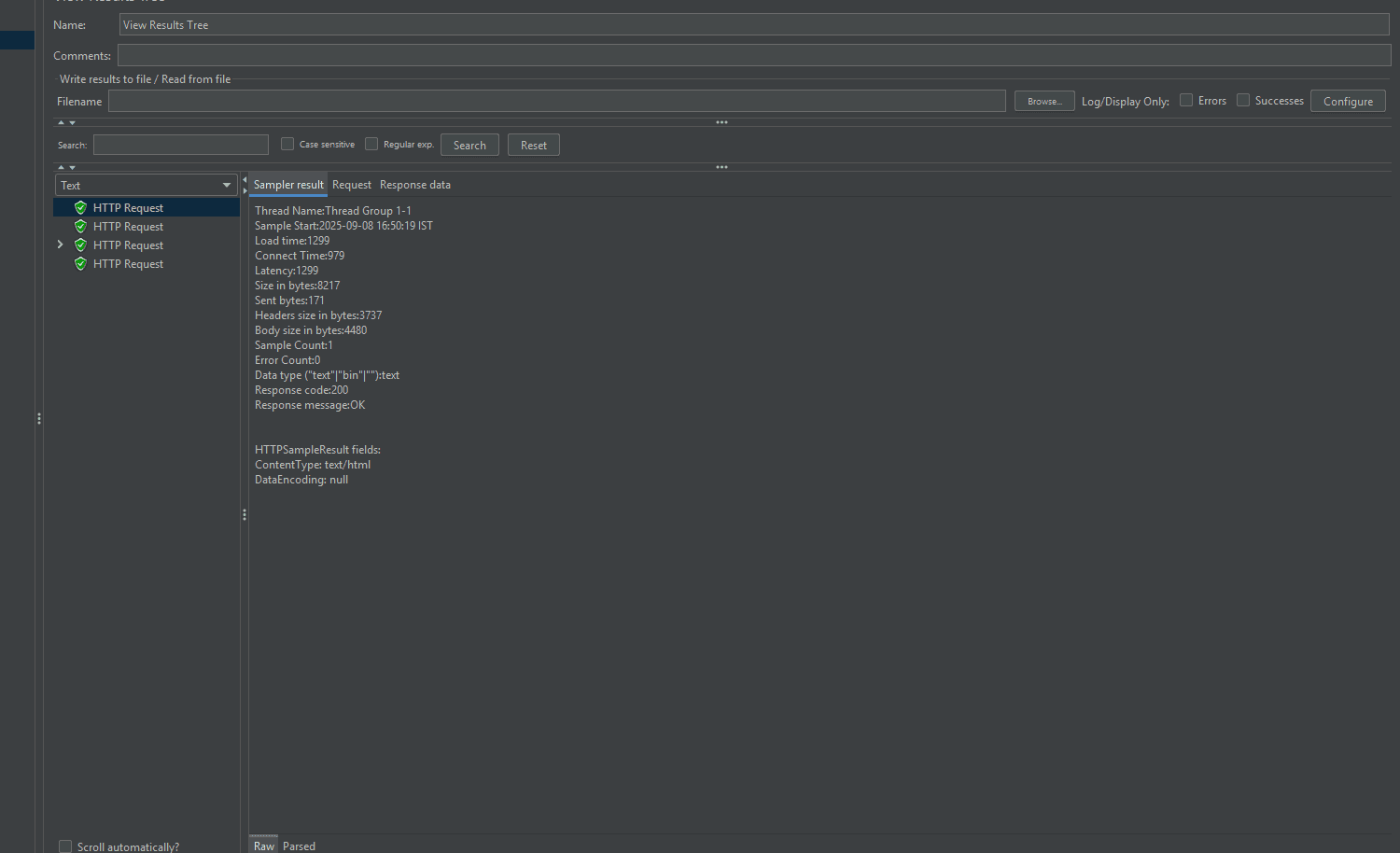
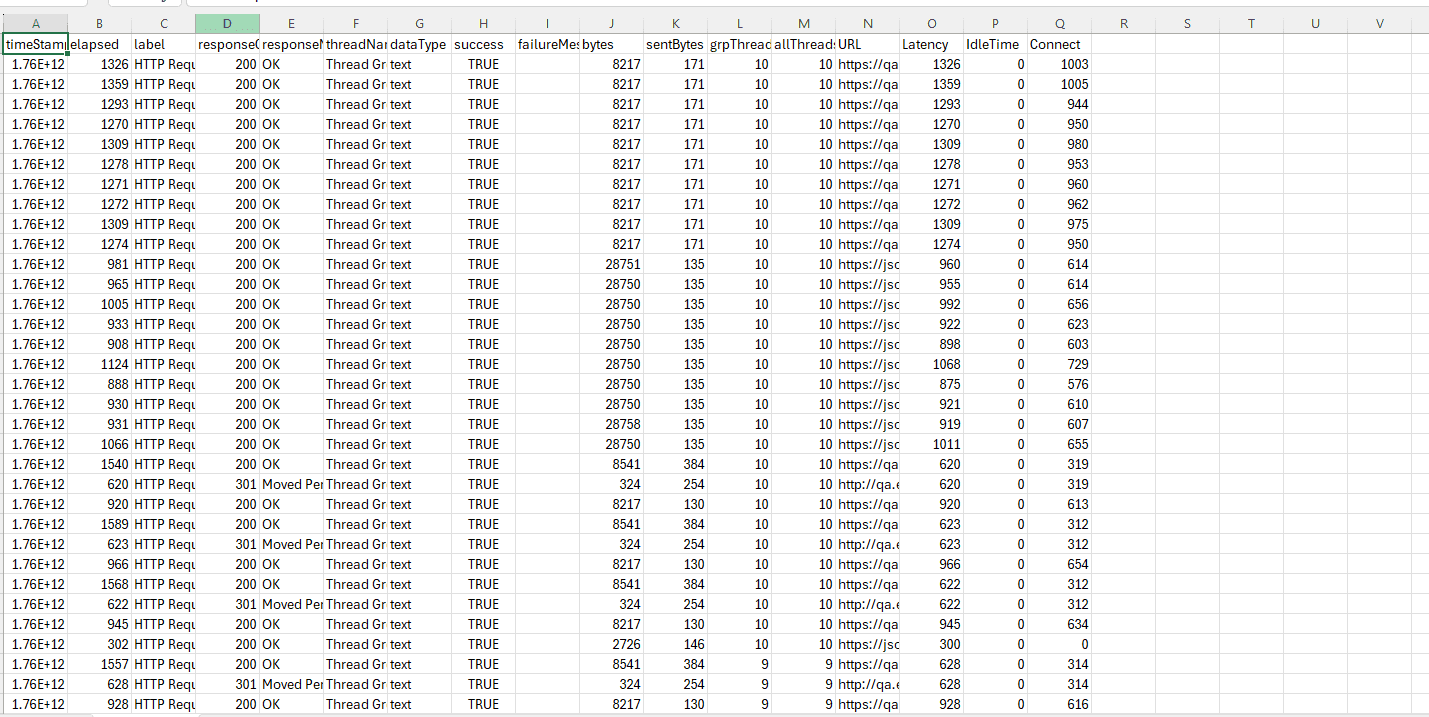
With listeners, you can analyze performance using graphs, tables, and logs.
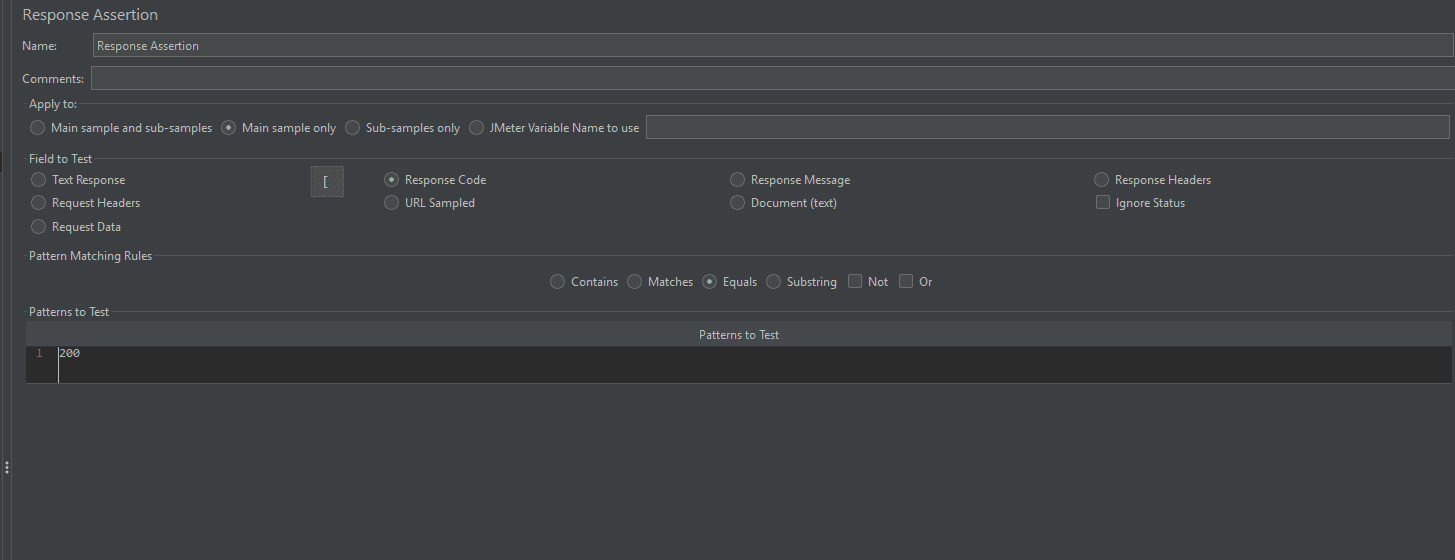
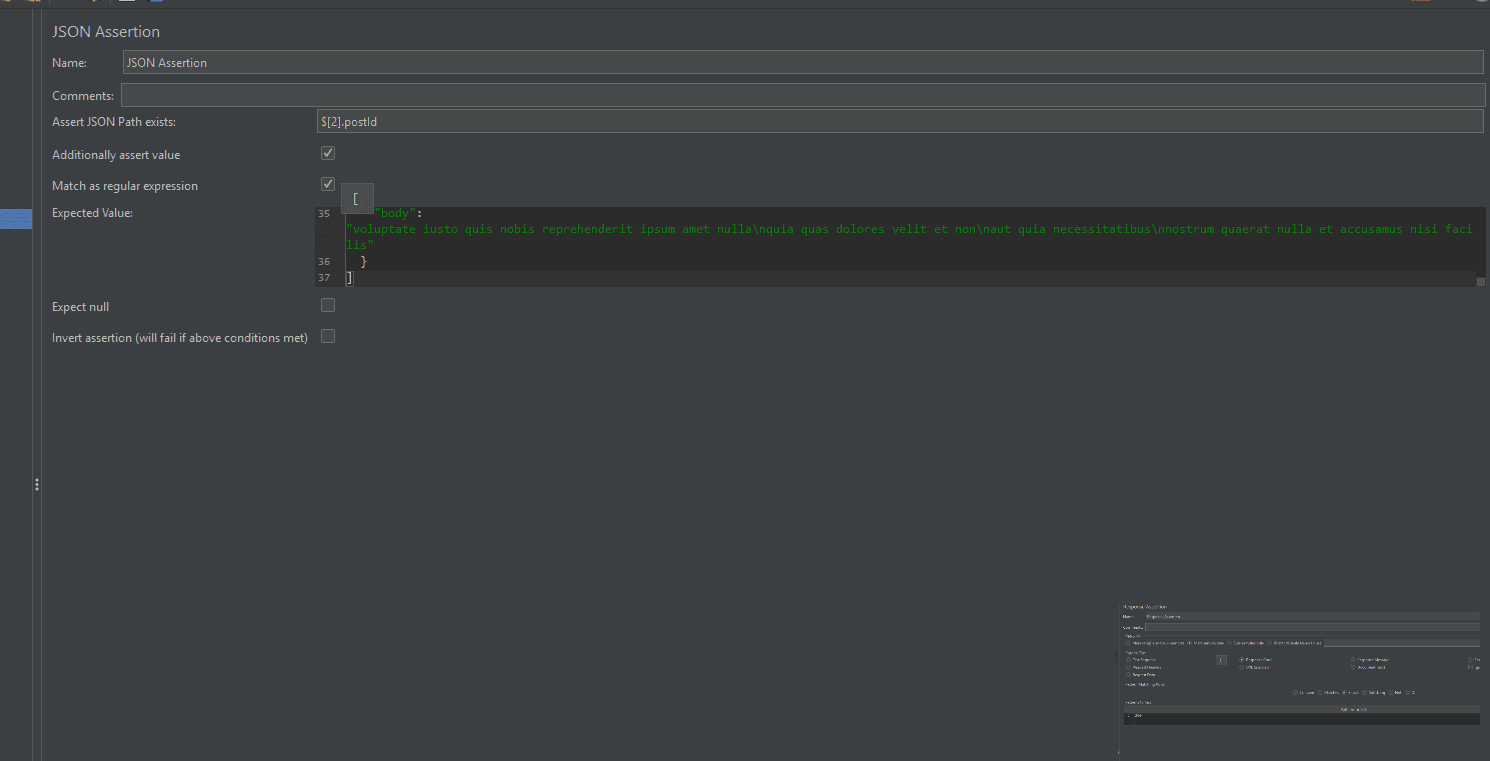
**4. Assertions :Assertions are used forvalidating server responses.**They ensure that your application returns the correct data. If an assertion fails, JMeter highlights it, helping testers catch issues quickly.
Conclusion
Apache JMeter is a versatile and widely used performance testing tool that supports multiple protocols, making it suitable for testing web applications, databases, services, and servers. By leveraging its Test Plan structure, testers can simulate real-world scenarios, validate responses with Assertions, and analyze results with Listeners.
Whether you’re testing application scalability or ensuring performance under heavy load, JMeter is an essential tool in every QA engineer’s toolkit.
