- Authors
- Written by :
- Name
- Varun Kumar
How we used AWS to run serverless cron jobs
- Published on
- Published On:
Cron jobs are incredibly helpful for automating routine tasks on a server or system. Here are some ways they can be beneficial:
- Regular Maintenance: Cron jobs can be used to schedule routine maintenance tasks such as cleaning up temporary files, optimizing databases, and updating system packages. This helps ensure the system's health and performance over time.
- Backup and Data Management: Automating backups of critical data and configuration files at regular intervals can prevent data loss in case of hardware failures or other emergencies. Cron jobs can be set up to create backups and manage the storage of old backup files.
- Log Rotation: Servers generate various log files that can quickly consume disk space. Cron jobs can rotate log files by compressing or moving old logs to archive directories, ensuring that logs don't fill up the disk.
- Scheduled Script Execution: Cron jobs can execute scripts that perform specific tasks, such as fetching data from external sources, processing data, and sending reports or notifications. This is particularly useful for repetitive tasks that need to be performed at specific times.
- Updating Software: Regularly updating software and applying security patches is crucial for maintaining system security. Cron jobs can automate the process of checking for and installing updates to the operating system and software packages.
- Web Content Updates: For websites or web applications, cron jobs can update content, refresh caches, and perform other tasks to keep the site's information up-to-date.
- Automated Testing: Developers can use cron jobs to schedule automated testing scripts, ensuring that code changes do not introduce new bugs or issues.
- Resource Management: Cron jobs can help manage server resources by adjusting system parameters, such as cleaning up memory caches, restarting services, or managing CPU usage.
- Security and Monitoring: Cron jobs can be used to perform security scans, monitor system resources, and generate alerts in case of abnormal conditions, enhancing the overall security and stability of the system.
- Custom Administrative Tasks: System administrators can use cron jobs to automate their own administrative tasks, tailored to the specific needs of the system and organization.
Overall, cron jobs streamline system management by reducing the need for manual intervention in routine tasks. They ensure consistency, save time, and reduce the risk of human error that can occur when tasks are performed manually.
For a very long time, when we think of running cron jobs, here’s what comes to our mind:
Step 1: Writing code / bash script - make sure it is executable
Step 2: Deploy it on a server / computer
Step 3: Use cron daemon of the server to execute the cron jobs on schedule
That basically means we need a server to run the cron daemon using which we will execute our scheduled job.
But with ever-increasing umbrella of cloud services provided by AWS, it is possible to create, deploy and execute cron jobs on AWS combining the following services:
| Service | Purpose |
|---|---|
| AWS Lambda | To write the code that we want to run on scheduled basis. |
| Amazon EventBridge Scheduler | To setup a serverless scheduler on AWS cloud, that will be used to execute the code on scheduled basis. |
For this blog we will be taking real-world example of one of our client projects. Here we are running serverless cron job to take the latest geo-location of drivers’ from a real-time location tracking integration and update them in our database for further processing. A diagram to explain the setup:
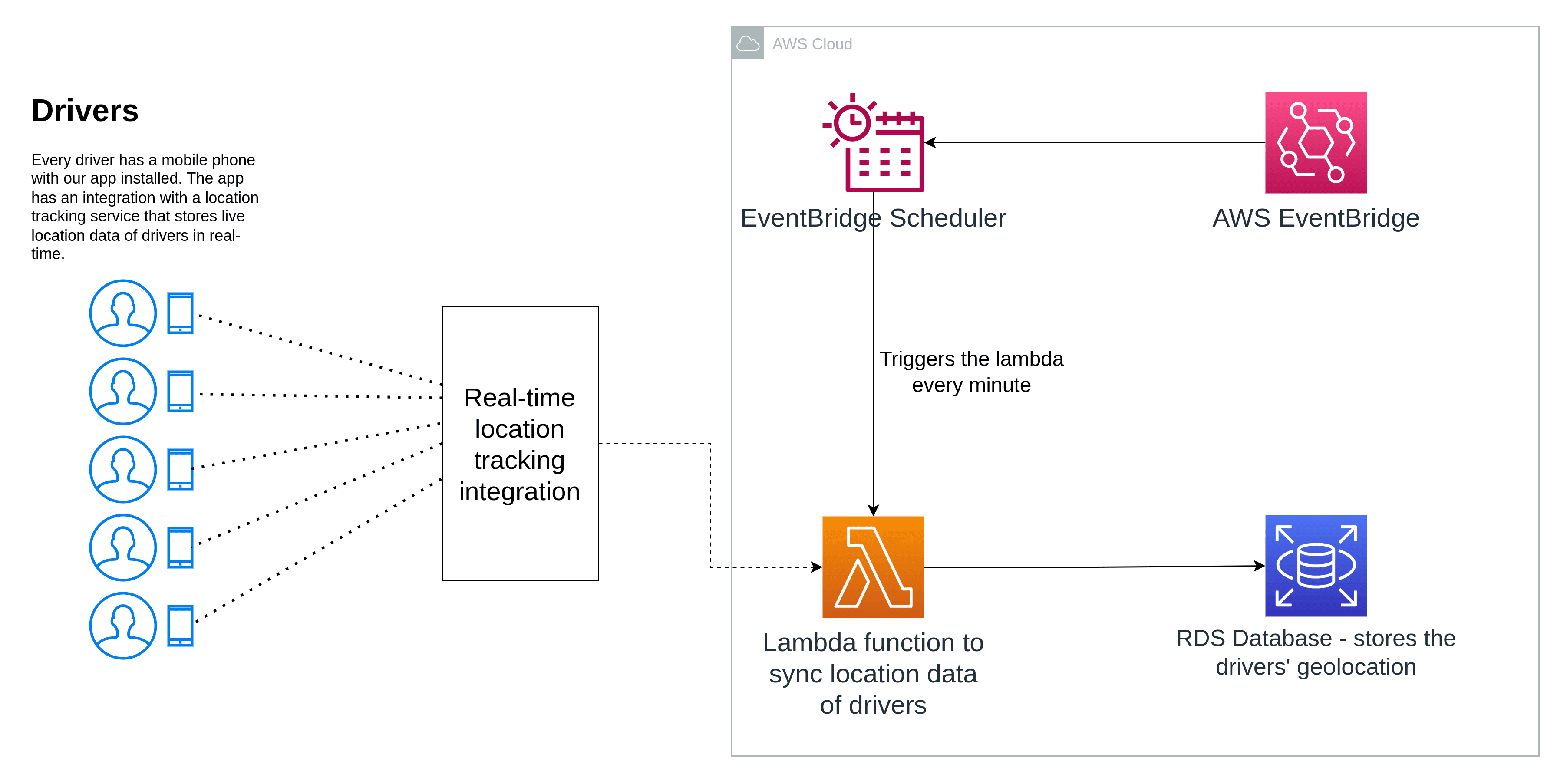
Writing the code - AWS Lambda
AWS Lambda is a serverless computing service which allows you to run our code without provisioning or managing servers. With AWS Lambda, we can execute code in response to various events and triggers, such as changes in data, incoming HTTP requests, updates to files, or scheduled time intervals. In our case, we will use AWS Lambda to write the code that we want to run on a scheduled basis, as part of a serverless cron job.
Good thing about Lambda is that it natively supports the following programming languages:
- Java
- Go
- PowerShell
- Node.js
- C#
- Python
- Ruby
Which gives us flexibility of writing our code in our preferred language.
We wrote a Lambda function for our use case in Python 3 that:
- Hits a REST API (checkout our REST API design guidelines) of our real-time location tracking integration to get live locations of all active drivers
- Creates and run a bulk update query for our MySQL-based relational database powered by AWS RDS that updates live location of all active drivers
Here is a quick look at the Lambda we wrote:
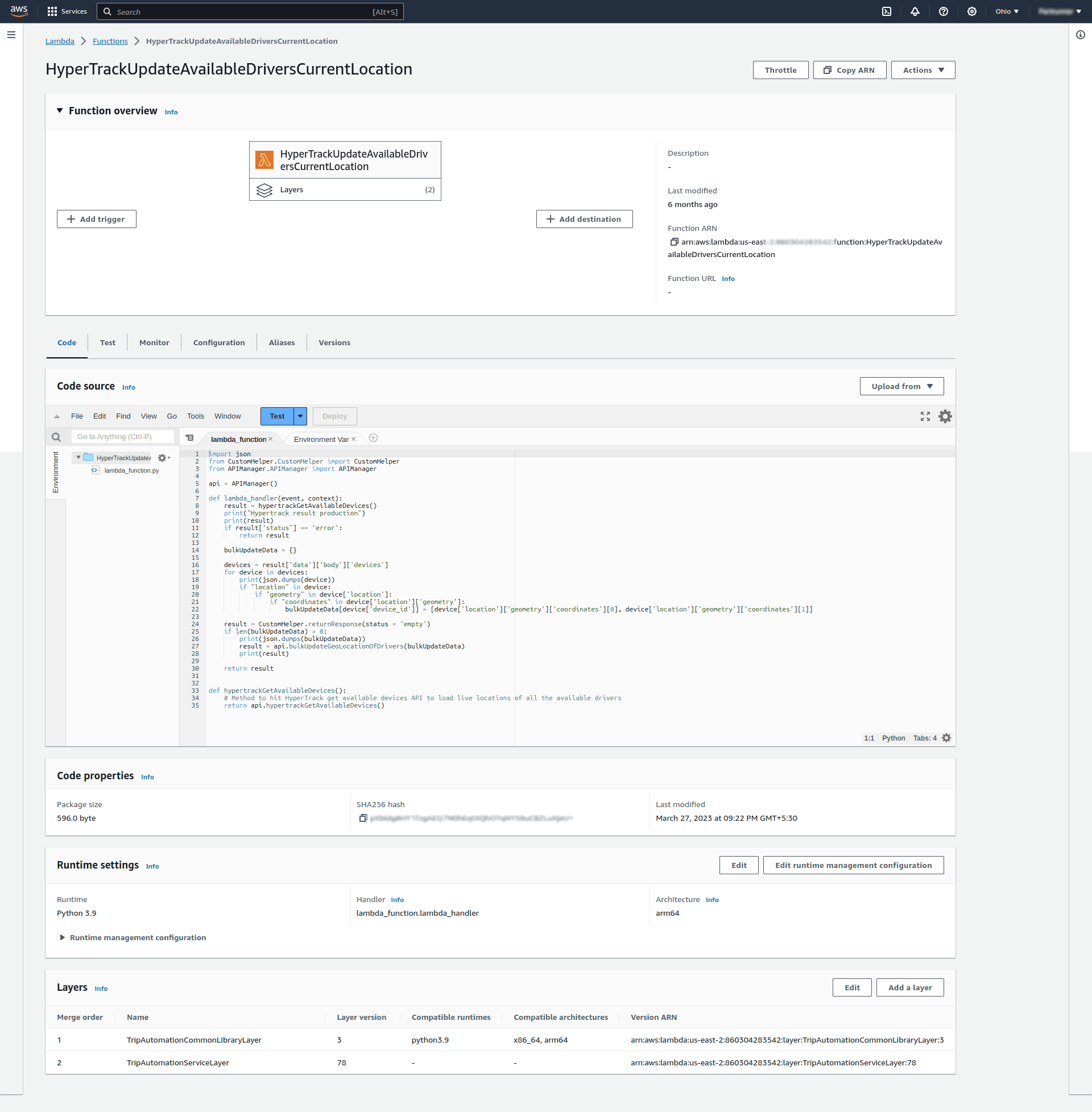
After writing the code in Lambda, we thoroughly tested our Lambda function to make sure it works as we expect.
Setting up a scheduler - Amazon EventBridge Scheduler
Once the Lambda code has been written and tested, we wanted to automatically trigger the Lambda at a regular time interval (every 1 minute in our case). Amazon EventBridge was our choice for creating this schedule.
Amazon EventBridge is a serverless event bus that enables us to build event-driven applications. It makes it easy to connect applications together and to respond to events in real time. EventBridge delivers a stream of real-time data from our applications, SaaS applications, and AWS services to targets such as AWS Lambda functions, HTTP invocation endpoints using API destinations, or event buses in other AWS accounts.
Here are some of the use cases for Amazon EventBridge:
- Building event-driven applications: EventBridge can be used to build event-driven applications that respond to events in real time. For example, we can use EventBridge to build a serverless application that sends a notification to a customer when an order is shipped.
- Integrating applications: EventBridge can be used to integrate applications together. For example, we can use EventBridge to send an event to a CRM system when a new customer signs up on the website.
- Automating workflows: EventBridge can be used to automate workflows. For example, we can use EventBridge to automatically start a new EC2 instance when a load balancer detects increased traffic.
Amazon EventBridge Scheduler is a serverless scheduler that enables us to create, run, and manage tasks from a central, managed service. It provides one-time and recurring scheduling functionality independent of event buses and rules. EventBridge Scheduler is highly customizable, and offers improved scalability over EventBridge scheduled rules, with a wider set of target API operations and AWS services.
EventBridge Scheduler can be used to schedule a variety of tasks, such as:
- Starting and stopping EC2 instances
- Running Lambda functions
- Sending emails
- Posting messages to SNS topics
- Invoking other API operations
To create a schedule, search “Amazon EventBridge” in AWS Management Console and navigate to the service:
Once on EventBridge Management Console, select “EventBridge Schedule” and click the button “Create Schedule”:
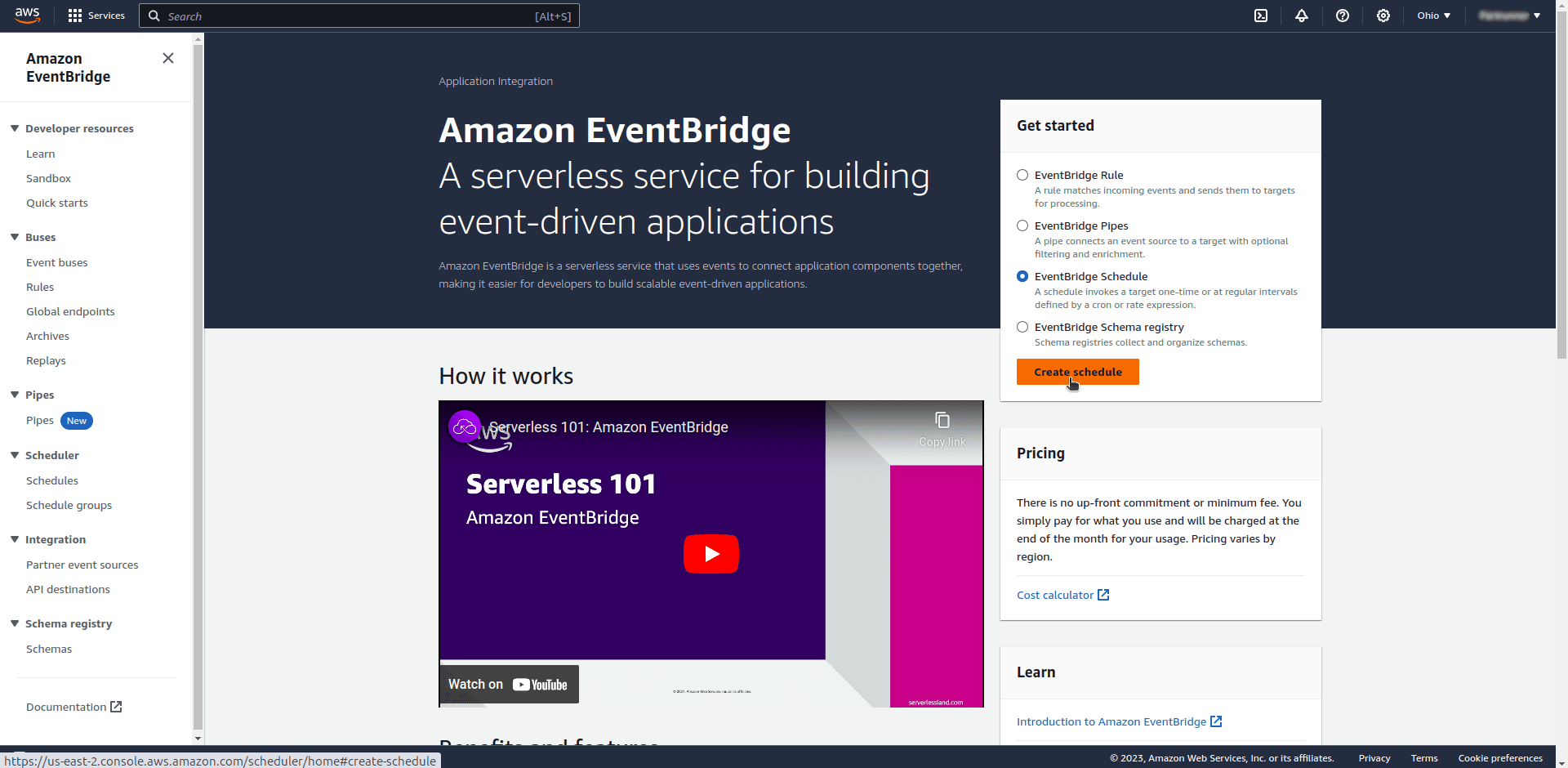
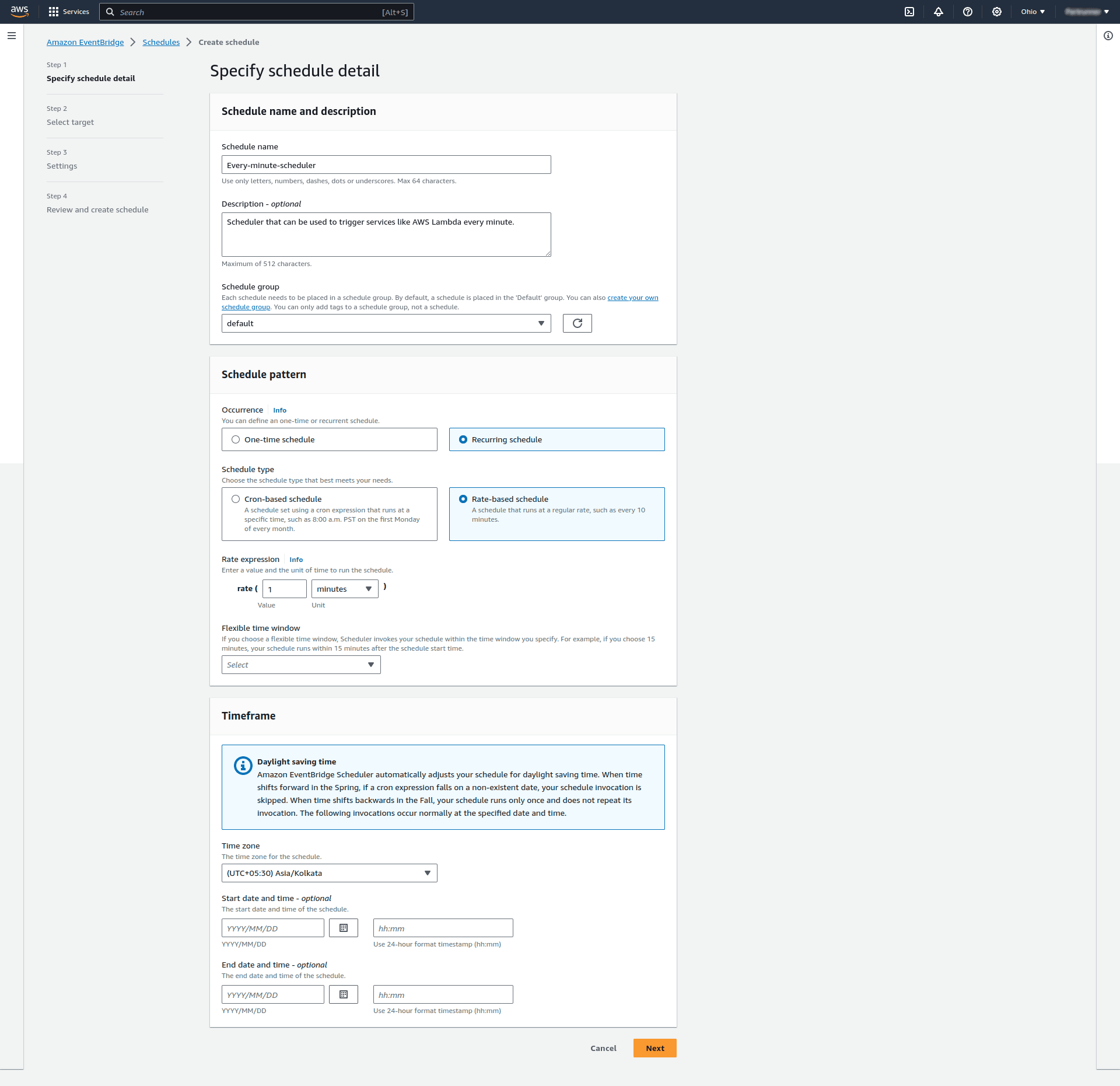
Next, we configure some basic details about the schedule. Notice the section Schedule pattern where EventBridge provides feature to create a recurring schedule. We configured it to run every minute:
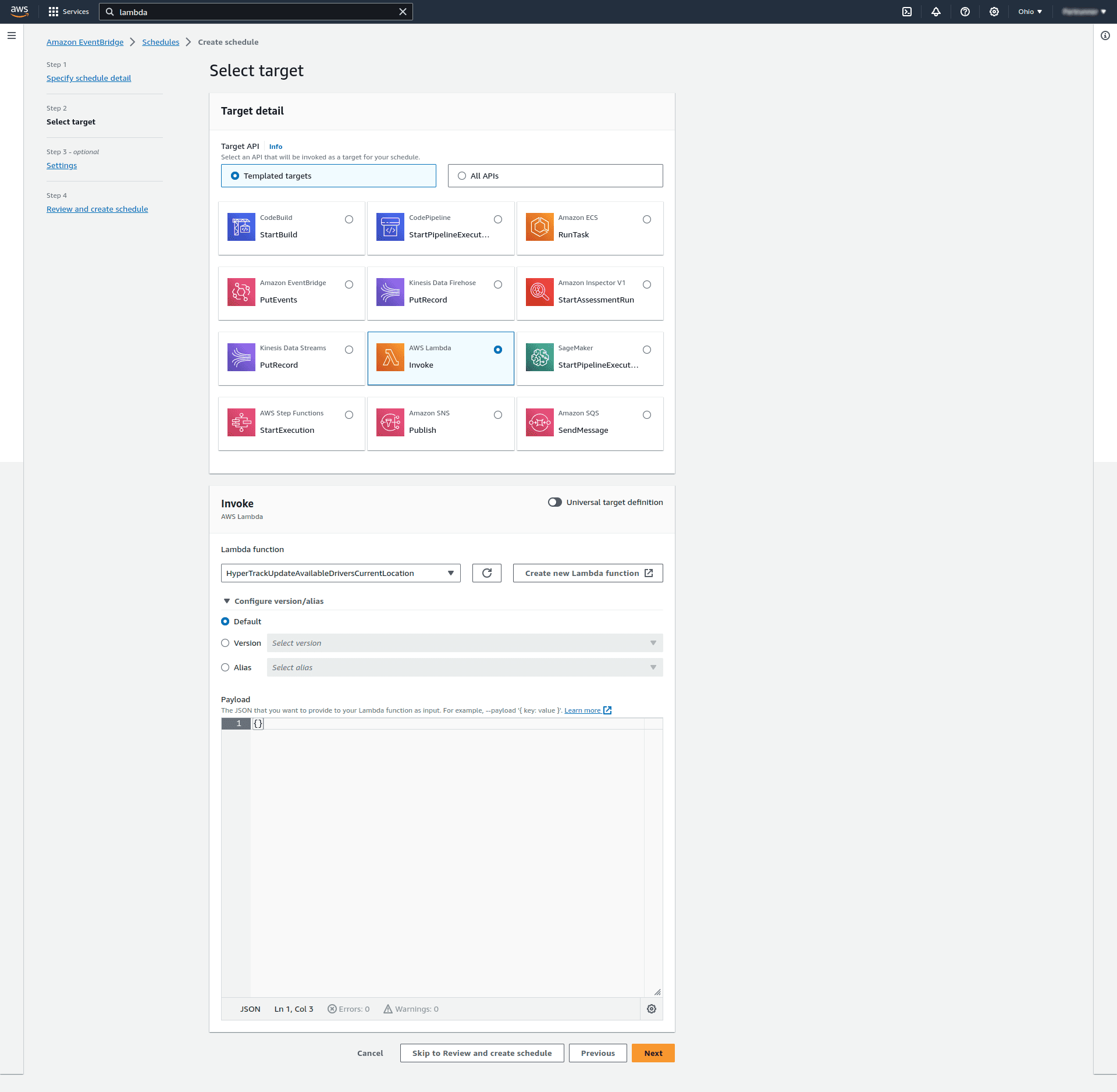
In next step we specified that we want to Invoke the Lambda function we created earlier. Notice that we can choose a variety of services apart from Lambda to be triggered on schedule:
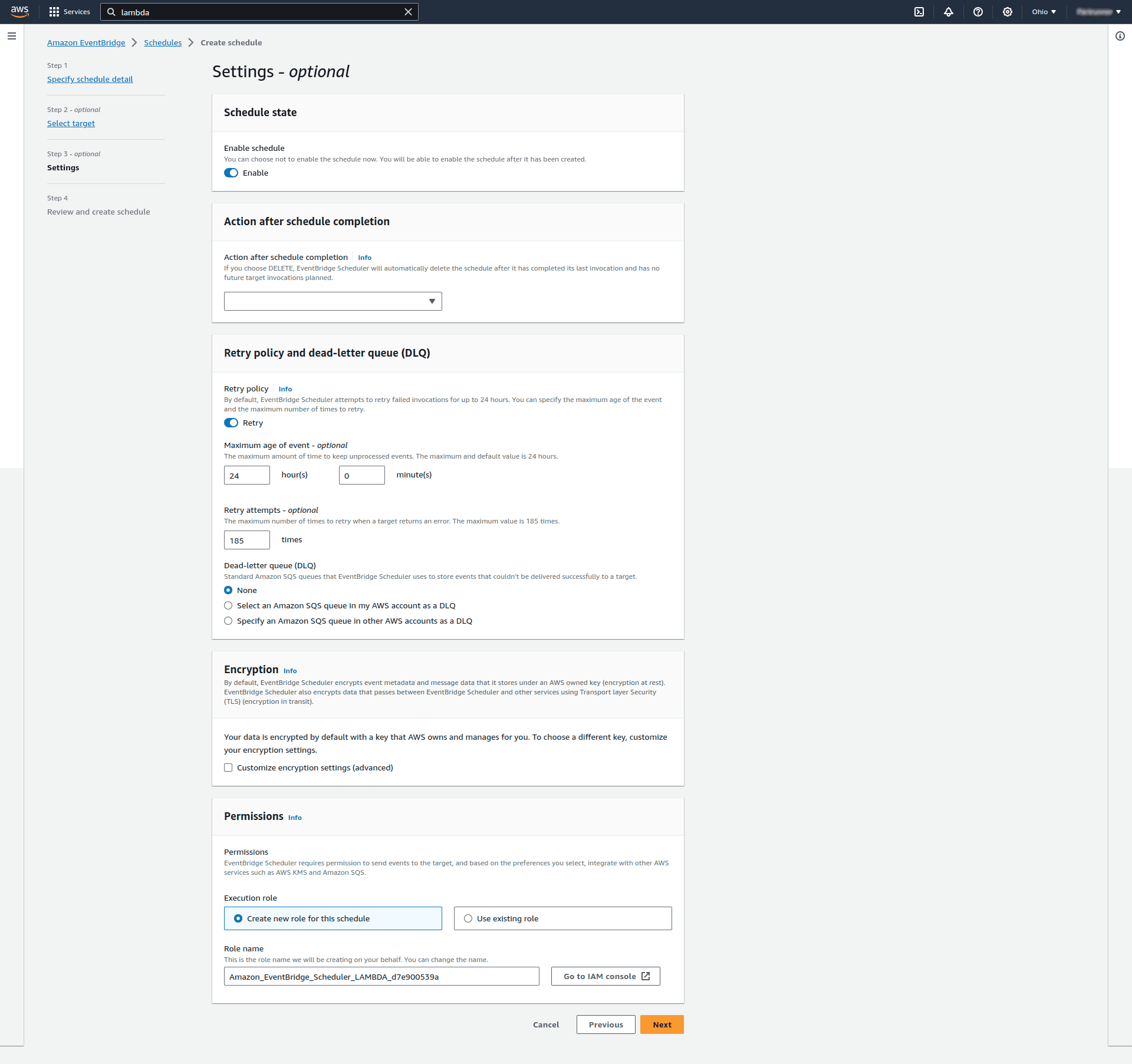
Next in Settings step, in Permissions section we have to have an appropriate permission role that will allow EventBridge to invoke the Lambda function:
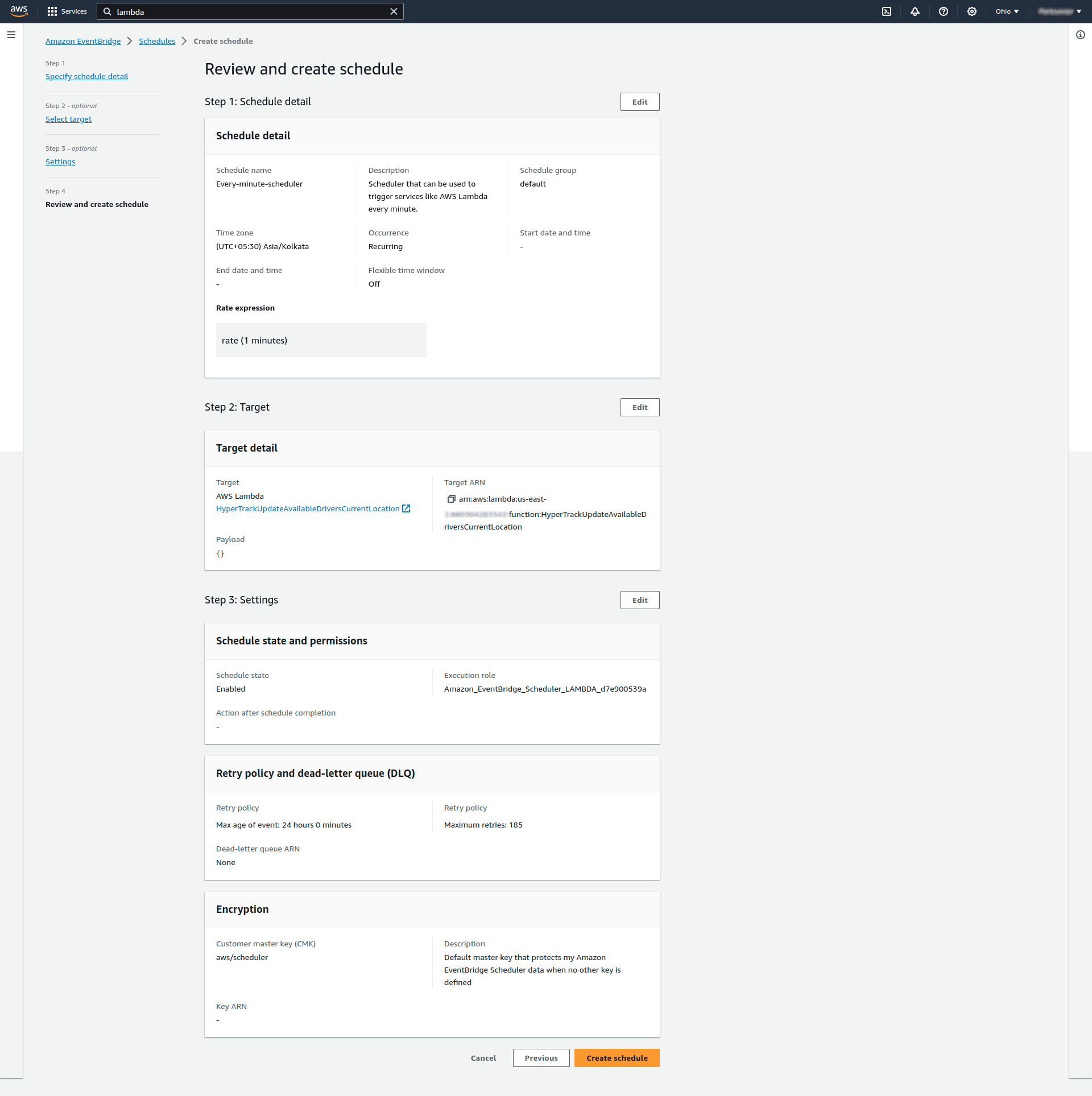
On the review page, we check everything is configured correctly. If all set, we successfully created the schedule:
And that's all that is required to create an automatic serverless scheduler that triggers our Lambda function.
Benefits of choosing this approach
Some of the key benefits why we created the above serverless solution instead of writing and running this cron job as part of main back-end project code on a back-end server:
No overload to run cron job on project's back-end servers
Had we created and running this cron job on the back-end server, it would be overloaded every minute due to the bulk data of hundreds of drivers’ location. The back-end server is only dedicated to handle the incoming API requests and returning the API responses.
Can be written and managed by different technical team
The core back-end logic in this project is written in PHP & Laravel. Since we can write Lambda functions in a variety of programming languages, the core back-end team can continue focus on their business logic, while a separate development team created the above Lambda with no involvement of the core back-end team.
I hope you found this blog useful. In conclusion, by embracing the latest technologies and practices outlined in this article, you can empower yourself to build more efficient, secure, and innovative solutions in the ever-evolving landscape of technology. Stay curious, keep learning, and continue to explore the limitless possibilities that the world of tech has to offer. Thanks!
